Transcriptional responses to biologically relevant doses of UV-B radiation in the model archaeon, Halobacterium sp. NRC-1
- PMID: 18759987
- PMCID: PMC2556686
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1448-4-13
Transcriptional responses to biologically relevant doses of UV-B radiation in the model archaeon, Halobacterium sp. NRC-1
Abstract
Background: Most studies of the transcriptional response to UV radiation in living cells have used UV doses that are much higher than those encountered in the natural environment, and most focus on short-wave UV (UV-C) at 254 nm, a wavelength that never reaches the Earth's surface. We have studied the transcriptional response of the sunlight-tolerant model archaeon, Halobacterium sp. NRC-1, to low doses of mid-wave UV (UV-B) to assess its response to UV radiation that is likely to be more biologically relevant.
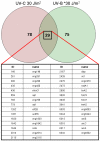
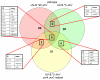
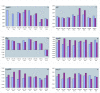
Results: Halobacterium NRC-1 cells were irradiated with UV-B at doses equivalent to 30 J/m2 and 5 J/m2 of UV-C. Transcriptional profiling showed that only 11 genes were up-regulated 1.5-fold or more by both UV-B doses. The most strongly up-regulated gene was radA1 (vng2473), the archaeal homologue of RAD51/recA recombinase. The others included arj1 (vng779) (recJ-like exonuclease), top6A (vng884) and top6B (vng885) (coding for Topoisomerase VI subunits), and nrdJ (vng1644) (which encodes a subunit of ribonucleotide reductase). We have found that four of the consistently UV-B up-regulated genes, radA1 (vng2473), vng17, top6B (vng885) and vng280, share a common 11-base pair motif in their promoter region, TTTCACTTTCA. Similar sequences were found in radA promoters in other halophilic archaea, as well as in the radA promoter of Methanospirillum hungatei. We analysed the transcriptional response of a repair-deficient DeltauvrA (vng2636) DeltauvrC (vng2381) double-deletion mutant and found common themes between it and the response in repair proficient cells.
Conclusion: Our results show a core set of genes is consistently up-regulated after exposure to UV-B light at low, biologically relevant doses. Eleven genes were up-regulated, in wild-type cells, after two UV-B doses (comparable to UV-C doses of 30 J/m2 and 5 J/m2), and only four genes were up-regulated by all doses of UV-B and UV-C that we have used in this work and previously. These results suggest that high doses of UV-C radiation do not necessarily provide a good model for the natural response to environmental UV. We have found an 11-base pair motif upstream of the TATA box in four of the UV-B up-regulated genes and suggest that this motif is the binding site for a transcriptional regulator involved in their response to UV damage in this model archaeon.
Figures
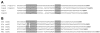
References
-
- Perdiz D, Grof P, Mezzina M, Nikaido O, Moustacchi E, Sage E. Distribution and repair of bipyrimidine photoproducts in solar UV-irradiated mammalian cells. Possible role of Dewar photoproducts in solar mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:26732–26742. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

