An immunosuppressed Syrian golden hamster model for SARS-CoV infection
- PMID: 18760437
- PMCID: PMC3722600
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.07.026
An immunosuppressed Syrian golden hamster model for SARS-CoV infection
Abstract
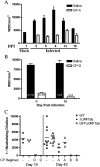
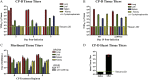
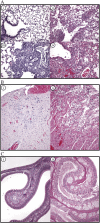
Several small animal models have been developed for the study of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) replication and pathogenesis. Syrian golden hamsters are among the best small animal models, though little clinical illness and no mortality are observed after virus infection. Cyclophosphamide was used to immunosuppress hamsters leading to a prolonged disease course and higher mortality after SARS-CoV infection. In addition, there was a significant weight loss, expanded tissue tropism, and increased viral pathology in the lung, heart, kidney, and nasal turbinate tissues. Infection with recombinant SARS-CoV viruses bearing disruptions in the gene 7 coding region showed no significant change in replication kinetics, tissue tropism, morbidity, or mortality suggesting that the ORF7a (7a) and ORF7b (7b) proteins are not required for virus replication in immunosuppressed hamsters. This modified hamster model may provide a useful tool for SARS-CoV pathogenesis studies, evaluation of antiviral therapy, and analysis of additional SARS-CoV mutants.
Figures

References
-
- Blandford G., Charlton D. Studies of pulmonary and renal immunopathology after nonlethal primary sendai viral infection in normal and cyclophosphamide-treated hamsters. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1977;115(2):305–314. - PubMed
-
- CDC Revised U.S. surveillance case definition for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and update on SARS cases—United States and worldwide, December 2003. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2003;52(49):1202–1206. - PubMed
-
- Chan W.M., Kwan Y.W., Wan H.S., Leung C.W., Chiu M.C. Epidemiologic linkage and public health implication of a cluster of severe acute respiratory syndrome in an extended family. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2004;23(12):1156–1159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

