Elevated autoantibody content in rheumatoid arthritis synovia with lymphoid aggregates and the effect of rituximab
- PMID: 18761748
- PMCID: PMC2592782
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2497
Elevated autoantibody content in rheumatoid arthritis synovia with lymphoid aggregates and the effect of rituximab
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to quantitatively evaluate the contribution of synovial lymphoid aggregates to autoantibody (rheumatoid factor [RF] and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide [anti-CCP]) and total immunoglobulin (IgG and IgM) production in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and the effect thereon of the B-cell-depleting antibody, rituximab, in the ARISE (Assessment of Rituximab's Immunomodulatory Synovial Effects) trial.
Methods: Autoantibodies as well as total IgM and IgG were quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in extracts of synovial tissues and matched serum from patients with RA or osteoarthritis (OA). Synovial biopsies and serum were obtained at baseline and 8 weeks following rituximab therapy in 14 RA patients. A synovial/serum index (SSI) was calculated as the ratio of synovial to serum antibody/albumin, with values above 1 representing synovial enrichment. Lymphoid aggregates were evaluated histologically.
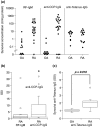
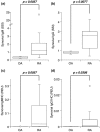
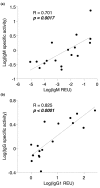
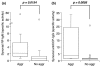
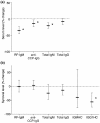
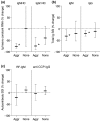
Results: Anti-CCP IgG, but not RF-IgM, was significantly enriched in RA synovia compared with serum. Total IgM and IgG were also enriched in RA, but not in OA. SSI correlated significantly with mRNA content for both IgM and IgG, demonstrating that it reflected synovial immunoglobulin production. RA synovia with lymphocyte aggregates contained significantly elevated RF-IgM and anti-CCP IgG compared with tissues with diffuse lymphoid infiltration. Rituximab treatment did not affect synovial autoantibody or total immunoglobulin SSI overall. However, in aggregate-containing tissues, rituximab significantly reduced total IgM and IgG SSI as well as IgM and IgG1 mRNA. Surprisingly, RF-IgM and anti-CCP IgG SSIs were unchanged by rituximab in aggregate-containing synovia.
Conclusions: Combined with earlier observations that synovial lymphoid aggregates are unaltered by rituximab treatment, these data suggest that lymphoid aggregates may provide a protective niche for autoantibody-producing cells.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00147966.
Figures

References
-
- Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, de Jong BA, Berglin E, Hallmans G, Wadell G, Stenlund H, Sundin U, van Venrooij WJ. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide and IgA rheumatoid factor predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2741–2749. doi: 10.1002/art.11223. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Klareskog L, Stolt P, Lundberg K, Kallberg H, Bengtsson C, Grunewald J, Ronnelid J, Harris HE, Ulfgren AK, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, Eklund A, Padyukov L, Alfredsson L. A new model for an etiology of rheumatoid arthritis: smoking may trigger HLA-DR (shared epitope)-restricted immune reactions to autoantigens modified by citrullination. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:38–46. doi: 10.1002/art.21575. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

