Inhibition of specific HDACs and sirtuins suppresses pathogenesis in a Drosophila model of Huntington's disease
- PMID: 18762557
- PMCID: PMC2581431
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddn273
Inhibition of specific HDACs and sirtuins suppresses pathogenesis in a Drosophila model of Huntington's disease
Abstract
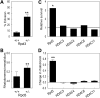
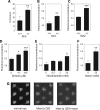
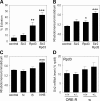
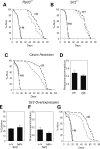
Huntington's disease (HD) is associated with transcriptional dysregulation, and multiple studies with histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors suggest that global approaches for restoring transcriptional balance and appropriate protein acetylation are therapeutically promising. To determine whether more targeted approaches might be effective, we have tested the impact of all the HDACs in Drosophila on Huntingtin (Htt)-induced pathology. Among the zinc-dependent or 'classic' HDACs, we find that neurodegeneration is most sensitive to levels of Rpd3. We also find that among the NAD(+)-dependent class III deacetylases, genetic or pharmacological reduction of either Sir2 or Sirt2 provides neuroprotection to Htt-challenged animals and that even greater neuroprotection is achieved when Rpd3 and Sir2 are simultaneously reduced. Our experiments suggest that longevity promoting strategies may be distinct from those that protect against neurodegeneration in Drosophila challenged with mutant human Htt. These results highlight a novel therapeutic approach for HD in the form of Sir2 inhibition and possible combinatorial inhibition of Sir2 and Rpd3.
Figures
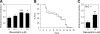
References
-
- Bates G., Harper P., Jones L. Huntington’s Disease. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2002.
-
- Shao J., Diamond M.I. Polyglutamine diseases: emerging concepts in pathogenesis and therapy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007;16(Spec no. 2):R115–R123. - PubMed
-
- Weydt P., La Spada A.R. Targeting protein aggregation in neurodegeneration – lessons from polyglutamine disorders. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 2006;10:505–513. - PubMed
-
- Marsh J., Thompson L. Can flies help humans treat neurodegenerative diseases? Bioessays. 2004;26:485–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

