Delayed maturation of an IL-12-producing dendritic cell subset explains the early Th2 bias in neonatal immunity
- PMID: 18762566
- PMCID: PMC2556775
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20071371
Delayed maturation of an IL-12-producing dendritic cell subset explains the early Th2 bias in neonatal immunity
Abstract
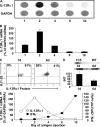
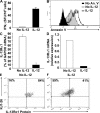
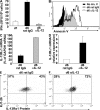
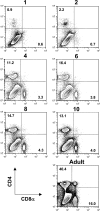
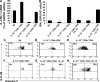
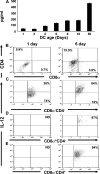
Primary neonatal T cell responses comprise both T helper (Th) cell subsets, but Th1 cells express high levels of interleukin 13 receptor alpha1 (IL-13R alpha 1), which heterodimerizes with IL-4R alpha. During secondary antigen challenge, Th2-produced IL-4 triggers the apoptosis of Th1 cells via IL-4R alpha/IL-13R alpha 1, thus explaining the Th2 bias in neonates. We show that neonates acquire the ability to overcome the Th2 bias and generate Th1 responses starting 6 d after birth. This transition was caused by the developmental maturation of CD8 alpha(+)CD4(-) dendritic cells (DCs), which were minimal in number during the first few days of birth and produced low levels of IL-12. This lack of IL-12 sustained the expression of IL-13R alpha 1 on Th1 cells. By day 6 after birth, however, a significant number of CD8 alpha(+)CD4(-) DCs accumulated in the spleen and produced IL-12, which triggered the down-regulation of IL-13R alpha 1 expression on Th1 cells, thus protecting them against IL-4-driven apoptosis.
Figures
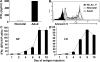

References
-
- Chen, N., and E.H. Field. 1995. Enhanced type 2 and diminished type 1 cytokines in neonatal tolerance. Transplantation. 59:933–941. - PubMed
-
- Forsthuber, T., H.C. Yip, and P.V. Lehmann. 1996. Induction of TH1 and TH2 immunity in neonatal mice. Science. 271:1728–1730. - PubMed
-
- Min, B., K.L. Legge, C. Pack, and H. Zaghouani. 1998. Neonatal exposure to a self-peptide–immunoglobulin chimera circumvents the use of adjuvant and confers resistance to autoimmune disease by a novel mechanism involving interleukin 4 lymph node deviation and interferon γ–mediated splenic anergy. J. Exp. Med. 188:2007–2017. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adkins, B., C. Leclerc, and S. Marshall-Clarke. 2004. Neonatal adaptive immunity comes of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:553–564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

