MGB probe assay for rapid detection of mtDNA11778 mutation in the Chinese LHON patients by real-time PCR
- PMID: 18763310
- PMCID: PMC2491690
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B0820058
MGB probe assay for rapid detection of mtDNA11778 mutation in the Chinese LHON patients by real-time PCR
Abstract
Objective: Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is a maternally inherited degeneration of the optic nerve caused by point mutations of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Many unsolved questions regarding the penetrance and pathophysiological mechanism of LHON demand efficient and reliable mutation testing. This study aims to develop a minor groove binder (MGB) probe assay for rapid detection of mtDNA11778 mutation and heteroplasmy in Chinese LHON patients by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
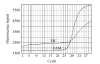
Methods: Forty-eight patients suspected of having LHON and their maternal relatives underwent a molecular genetic evaluation, with 20 normal individuals as a control group at the same time. A real-time PCR involving two MGB probes was used to detect the mtDNA11778 mutation and heteroplasmy. A linear standard curve was obtained by pUCmLHONG and pUCmLHONA clones.
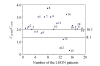
Results: All 48 LHON patients and their maternal relatives were positive for mtDNA11778 mutation in our assay, 27 heteroplasmic and 21 homoplasmic. Eighteen cases did not show an occurrence of the disease, while 9 developed the disease among the 27 heteroplasmic mutation cases. Eleven did not show an occurrence of the disease, while 10 cases developed the disease among 21 homoplasmic mutation cases. There was a significant difference in the incidence between the heteroplasmic and the homoplasmic mutation types. The time needed for running a real-time PCR assay was only 80 min.
Conclusion: This real-time PCR assay is a rapid, reliable method for mtDNA mutation detection as well as heteroplasmy quantification. Detecting this ratio is very important for predicting phenotypic expression of unaffected carriers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Detection of mtDNA*LHON G11778A mutation by real-time polymerase chain reaction using TaqMan-MGB probe technology].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Aug;42(8):728-32. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17081446 Chinese.
-
A simple oligonucleotide biochip capable of rapidly detecting known mitochondrial DNA mutations in Chinese patients with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON).Dis Markers. 2011;30(4):181-90. doi: 10.3233/DMA-2011-0767. Dis Markers. 2011. PMID: 21694444 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid quantification of the heteroplasmy of mutant mitochondrial DNAs in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy using the Invader technology.Clin Biochem. 2004 Apr;37(4):268-76. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2003.11.011. Clin Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15003728
-
[Past, present, and future in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001 Dec;105(12):809-27. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11802455 Review. Japanese.
-
[DNA diagnosis in the age of individual made-to-order medications].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004 Dec;108(12):863-85; discussion 886. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15656090 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of a novel PCR-RFLP based method for the detection of 3 primary mitochondrial mutations in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy patients.Eye Vis (Lond). 2015 Oct 25;2:18. doi: 10.1186/s40662-015-0028-0. eCollection 2015. Eye Vis (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26605371 Free PMC article.
-
Allele-specific RT-PCR for the rapid detection of recurrent SLC12A3 mutations for Gitelman syndrome.NPJ Genom Med. 2021 Aug 13;6(1):68. doi: 10.1038/s41525-021-00230-8. NPJ Genom Med. 2021. PMID: 34389731 Free PMC article.
-
A real-time ARMS PCR/high-resolution melt curve assay for the detection of the three primary mitochondrial mutations in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy.Mol Vis. 2016 Oct 12;22:1169-1175. eCollection 2016. Mol Vis. 2016. PMID: 27746671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinnery PF, Andrews RM, Turnbull DM, Howell NN. Leber hereditary optic neuropathy: does heteroplasmy influence the inheritance and expression of the G11778A mitochondrial DNA mutation? Am J Med Genet. 2001;98(3):235–243. doi: 10.1002/1096-8628(20010122)98:3<235::AID-AJMG1086>3.0.CO;2-O. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

