Delivery of small interfering RNA for inhibition of endothelial cell apoptosis by hypoxia and serum deprivation
- PMID: 18765230
- PMCID: PMC3957099
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.08.123
Delivery of small interfering RNA for inhibition of endothelial cell apoptosis by hypoxia and serum deprivation
Abstract
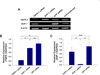
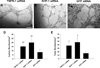
RNA interference (RNAi) for anti-angiogenic or pro-apoptotic factors in endothelial cells (ECs) has great potential for the treatment of ischemic diseases by promoting angiogenesis or inhibiting apoptosis. Here, we report the utility of small interfering RNA (siRNA) in inhibiting EC apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). siRNA was designed and synthesized targeting tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor-1 (TNFR-1) and Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1). Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were cultured under in vitro hypoxic and serum-deprived conditions to simulate in vivo ischemic conditions. Two days after liposomal delivery of siRNA targeting TNFR-1 and SHP-1, significant silencing of each target (TNFR-1; 76.5% and SHP-1; 97.2%) was detected. Under serum-deprived hypoxic (1% oxygen) conditions, TNF-alpha expression in HUVECs increased relative to normoxic (20% oxygen) and serum-containing conditions. Despite enhanced TNF-alpha expression, suppression of TNFR-1 or SHP-1 by siRNA delivery not only enhanced expression of angiogenic factors (KDR/Flk-1 and eNOS) and anti-apoptotic factor (Bcl-xL) but also reduced expression of a pro-apoptotic factor (Bax). Transfection of TNFR-1 or SHP-1 siRNA significantly decreased the HUVEC apoptosis while significantly enhancing HUVEC proliferation and capillary formation. The present study demonstrates that TNFR-1 and SHP-1 may be useful targets for the treatment of myocardial or hindlimb ischemia.
Figures


References
-
- Lee CN, Cheng WF, Chang MC, Su YN, Chen CA, Hsieh FJ. Hypoxia-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells and embryonic stem cells. Apoptosis. 2005;10:887–894. - PubMed
-
- Hogg N, Browning J, Howard T, Winterford C, Fitzpatrick D, Gobé G. Apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells caused by serum deprivation, oxidative stress and transforming growth factor-beta. Endothelium. 1999;7:35–49. - PubMed
-
- Matsushita H, Morishita R, Nata T, Aoki M, Nakagami H, Taniyama Y, Yamamoto K, Higaki J, Yasufumi K, Ogihara T. Hypoxia-induced endothelial apoptosis through nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB)-mediated bcl-2 suppression: in vivo evidence of the importance of NF-kappaB in endothelial cell regulation. Circ. Res. 2000;86:974–981. - PubMed
-
- Meeson AP, Argilla M, Ko K, Witte L, Lang RA. VEGF deprivation-induced apoptosis is a component of programmed capillary regression. Development. 1999;126:1407–1415. - PubMed
-
- Nakagami H, Cui TX, Iwai M, Shiuchi T, Takeda-Matsubara Y, Wu L, Horiuchi M. Tumor necrosis factor-α inhibits growth factor-mediated cell proliferation through SHP-1 activation in endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002;22:238–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

