Images in cardiovascular medicine. Healing of an asymptomatic carotid plaque ulceration
- PMID: 18765382
- PMCID: PMC2703661
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.764779
Images in cardiovascular medicine. Healing of an asymptomatic carotid plaque ulceration
Figures
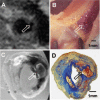

Similar articles
-
Images in cardiovascular medicine. Detection of carotid atherosclerotic plaque ulceration, calcification, and thrombosis by multicontrast weighted magnetic resonance imaging.Circulation. 2005 Jul 5;112(1):e3-4. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.494419. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 15998688 No abstract available.
-
Detection of carotid artery stenosis using histological specimens: a comparison of CT angiography, magnetic resonance angiography, digital subtraction angiography and Doppler ultrasonography.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2016 Aug;158(8):1505-14. doi: 10.1007/s00701-016-2842-0. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2016. PMID: 27255656
-
Carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic plaque.Neurol Clin. 2006 Nov;24(4):661-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2006.06.005. Neurol Clin. 2006. PMID: 16935194 Review.
-
Feasibility of Preoperative Magnetic Resonance Angiography/Black-Blood Magnetic Resonance Imaging/Computed Tomography Fusion Imaging Without Contrast Agent for Carotid Endarterectomy.World Neurosurg. 2022 Nov;167:e1219-e1224. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2022.09.018. Epub 2022 Sep 8. World Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 36089271
-
Impact of plaque characterization on carotid interventions.Perspect Vasc Surg Endovasc Ther. 2006 Dec;18(4):312-5. doi: 10.1177/1531003506297196. Perspect Vasc Surg Endovasc Ther. 2006. PMID: 17351197 Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetization transfer magnetic resonance of human atherosclerotic plaques ex vivo detects areas of high protein density.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2011 Nov 22;13(1):73. doi: 10.1186/1532-429X-13-73. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2011. PMID: 22107813 Free PMC article.
-
Atherosclerosis, Periodontal Disease, and Treatment with Resolvins.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2017 Nov 6;19(12):57. doi: 10.1007/s11883-017-0696-4. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2017. PMID: 29110146 Review.
-
Cervical Carotid Plaque MRI : Review of Atherosclerosis Imaging Features and their Histologic Underpinnings.Clin Neuroradiol. 2021 Jun;31(2):295-306. doi: 10.1007/s00062-020-00987-y. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Clin Neuroradiol. 2021. PMID: 33398451 Review.
-
Characterization of healing following atherosclerotic carotid plaque rupture in acutely symptomatic patients: an exploratory study using in vivo cardiovascular magnetic resonance.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2011 Oct 27;13(1):64. doi: 10.1186/1532-429X-13-64. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2011. PMID: 22032404 Free PMC article.
-
A robust rabbit model of human atherosclerosis and atherothrombosis.J Lipid Res. 2009 May;50(5):787-97. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800460-JLR200. Epub 2009 Jan 12. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 19141434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burke AP, Kolodgie FD, Farb A, Weber DK, Malcom GT, Smialek J, Virmani R. Healed plaque ruptures and sudden coronary death: evidence that subclinical rupture has a role in plaque progression. Circulation. 2001;103:934–940. - PubMed
-
- Holmes JW, Yamashita H, Waldman LK, Covell JW. Scar remodeling and transmural deformation after infarction in the pig. Circulation. 1994;90:411–420. - PubMed
-
- Chu B, Yuan C, Takaya N, Shewchuk JR, Clowes AW, Hatsukami TS. Serial high-spatial-resolution, multisequence magnetic resonance imaging studies identify fibrous cap rupture and penetrating ulcer into carotid atherosclerotic plaque. Circulation. 2006;113:e660–e661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

