Treatment of metastatic melanoma using interleukin-2 alone or in conjunction with vaccines
- PMID: 18765555
- PMCID: PMC2656367
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0116
Treatment of metastatic melanoma using interleukin-2 alone or in conjunction with vaccines
Abstract
Purpose: To identify prognostic factors associated with survival beyond 4 years and overall response in patients with metastatic melanoma treated with high-dose bolus i.v. interleukin-2 (IL-2) given either alone or in combination with a variety of melanoma vaccines.
Study design: 684 consecutive patients with metastatic melanoma received high-dose bolus i.v. IL-2 either alone or in conjunction with a variety of melanoma vaccines. Treatments occurred between August 1, 1985 and January 1, 2006.
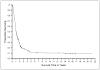
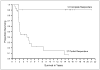
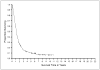
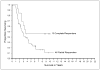
Results: The overall objective response rate was 13% for patients receiving IL-2 alone and 16% for patients who received IL-2 with vaccine. In patients treated with IL-2 alone (n=305) and IL-2 with vaccine (n=379), having an objective response was associated with survival beyond 4 years (P<0.0001). No pretreatment factors could be identified that were strongly associated with increased rate of objective response or long-term survival in patients receiving IL-2 alone. In patients receiving IL-2 with vaccines, there were increased response rates in patients with s.c. or cutaneous disease only and lower response rates with visceral disease only. Patients who received the gp100:209-217(210M) peptide plus IL-2 showed a strong trend to increased objective responses compared with IL-2 alone (22% versus 12.8%; P=0.01) and also compared with patients who received a variety of vaccines that did not include this immunogenic peptide (13.8%; P=0.009).
Conclusion: IL-2 can produce a modest response rate in patients with metastatic melanoma including patients with durable complete responses. S.c. or cutaneous disease only and vaccination with gp100:209-217(210M) peptide was associated with significant increase in response rates.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66. - PubMed
-
- Balch CM, Atkins MB, Sober AJ. Cutaneous melanoma. In: Devita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, editors. Cancer. Principles & practice of oncology. 7. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven Publishers; 2005. p. 1754.
-
- Atkins MB, Lotze MT, Dutcher JP, et al. High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: analysis of 270 patients treated between 1985 and 1993. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2105–16. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Topalian SL, et al. Treatment of 283 consecutive patients with metastatic melanoma or renal cell cancer using high-dose bolus interleukin 2. JAMA. 1994;271:907–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

