Transcription of multiple yeast ribosomal DNA genes requires targeting of UAF to the promoter by Uaf30
- PMID: 18765638
- PMCID: PMC2573240
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00703-08
Transcription of multiple yeast ribosomal DNA genes requires targeting of UAF to the promoter by Uaf30
Abstract
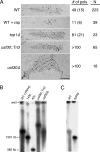
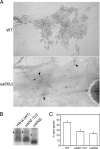
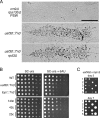
Upstream activating factor (UAF) is a multisubunit complex that functions in the activation of ribosomal DNA (rDNA) transcription by RNA polymerase I (Pol I). Cells lacking the Uaf30 subunit of UAF reduce the rRNA synthesis rate by approximately 70% compared to wild-type cells and produce rRNA using both Pol I and Pol II. Miller chromatin spreads demonstrated that even though there is an overall reduction in rRNA synthesis in uaf30 mutants, the active rDNA genes in such strains are overloaded with polymerases. This phenotype was specific to defects in Uaf30, as mutations in other UAF subunits resulted in a complete absence of rDNA genes with high or even modest Pol densities. The lack of Uaf30 prevented UAF from efficiently binding to the rDNA promoter in vivo, leading to an inability to activate a large number of rDNA genes. The relatively few genes that did become activated were highly transcribed, apparently to compensate for the reduced rRNA synthesis capacity. The results show that Uaf30p is a key targeting factor for the UAF complex that facilitates activation of a large proportion of rDNA genes in the tandem array.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Alternative chromatin structures of the 35S rRNA genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae provide a molecular basis for the selective recruitment of RNA polymerases I and II.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Apr;30(8):2028-45. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01512-09. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20154141 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription of chromosomal rRNA genes by both RNA polymerase I and II in yeast uaf30 mutants lacking the 30 kDa subunit of transcription factor UAF.EMBO J. 2001 Aug 15;20(16):4512-21. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.16.4512. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11500378 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor UAF, expansion and contraction of ribosomal DNA (rDNA) repeats, and RNA polymerase switch in transcription of yeast rDNA.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Dec;19(12):8559-69. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.12.8559. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10567580 Free PMC article.
-
How do cells count multi-copy genes?: "Musical Chair" model for preserving the number of rDNA copies.Curr Genet. 2019 Aug;65(4):883-885. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00956-0. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30904990 Review.
-
RNA polymerase I activation and hibernation: unique mechanisms for unique genes.Transcription. 2018;9(4):248-254. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2017.1416267. Epub 2018 Jan 26. Transcription. 2018. PMID: 29372670 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reconstitution of RNA Polymerase I Upstream Activating Factor and the Roles of Histones H3 and H4 in Complex Assembly.J Mol Biol. 2018 Mar 2;430(5):641-654. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Jan 31. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29357286 Free PMC article.
-
Psoralen Crosslinking-Chromatin Endogenous Cleavage Assay to Examine Histone DNA Interactions of Active and Inactive rRNA Genes.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2919:133-154. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4486-7_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40257561
-
Nascent Transcript Folding Plays a Major Role in Determining RNA Polymerase Elongation Rates.Mol Cell. 2020 Aug 6;79(3):488-503.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.06.002. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32585128 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative chromatin structures of the 35S rRNA genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae provide a molecular basis for the selective recruitment of RNA polymerases I and II.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Apr;30(8):2028-45. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01512-09. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20154141 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Coding, RNAPII-Dependent Transcription at the Promoters of rRNA Genes Regulates Their Chromatin State in S. cerevisiae.Noncoding RNA. 2021 Jul 11;7(3):41. doi: 10.3390/ncrna7030041. Noncoding RNA. 2021. PMID: 34287362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brachmann, C. B., A. Davies, G. J. Cost, E. Caputo, J. Li, P. Hieter, and J. D. Boeke. 1998. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 14115-132. - PubMed
-
- Buck, S. W., J. J. Sandmeier, and J. S. Smith. 2002. RNA polymerase I propagates unidirectional spreading of rDNA silent chromatin. Cell 1111003-1014. - PubMed
-
- Burke, D., D. Dawson, and T. Stearns. 2000. Methods in yeast genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
