Functional mapping of YadA- and Ail-mediated binding of human factor H to Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3
- PMID: 18765735
- PMCID: PMC2573320
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00314-08
Functional mapping of YadA- and Ail-mediated binding of human factor H to Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3
Abstract
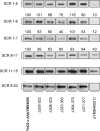
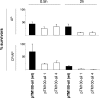
Yersinia enterocolitica is an enteric pathogen that exploits diverse means to survive in the human host. Upon Y. enterocolitica entry into the human host, bacteria sense and respond to variety of signals, one of which is the temperature. Temperature in particular has a profound impact on Y. enterocolitica gene expression, as most of its virulence factors are expressed exclusively at 37 degrees C. These include two outer membrane proteins, YadA and Ail, that function as adhesins and complement resistance (CR) factors. Both YadA and Ail bind the functionally active complement alternative pathway regulator factor H (FH). In this study, we characterized regions on both proteins involved in CR and the interaction with FH. Twenty-eight mutants having short (7 to 41 amino acids) internal deletions within the neck and stalk of YadA and two complement-sensitive site-directed Ail mutants were constructed to map the CR and FH binding regions of YadA and Ail. Functional analysis of the YadA mutants revealed that the stalk of YadA is required for both CR and FH binding and that FH appears to target several conformational and discontinuous sites of the YadA stalk. On the other hand, the complement-sensitive Ail mutants were not affected in FH binding. Our results also suggested that Ail- and YadA-mediated CR does not depend solely on FH binding.
Figures





References
-
- Areschoug, T., M. Stalhammar-Carlemalm, I. Karlsson, and G. Lindahl. 2002. Streptococcal beta protein has separate binding sites for human factor H and IgA-Fc. J. Biol. Chem. 27712642-12648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

