Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in thoracic aortic aneurysm development: a paradox in pathogenesis
- PMID: 18765947
- PMCID: PMC2645475
- DOI: 10.1159/000151766
Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in thoracic aortic aneurysm development: a paradox in pathogenesis
Abstract
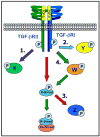
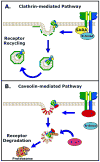
Thoracic aortic aneurysms (TAAs) are potentially devastating, and due to their asymptomatic behavior, pose a serious health risk characterized by the lack of medical treatment options and high rates of surgical morbidity and mortality. Independent of the inciting stimuli (biochemical/mechanical), TAA development proceeds by a multifactorial process influenced by both cellular and extracellular mechanisms, resulting in alterations of the structure and composition of the vascular extracellular matrix (ECM). While the role of enhanced ECM proteolysis in TAA formation remains undisputed, little attention has been focused on the upstream signaling events that drive the remodeling process. Recent evidence highlighting the dysregulation of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) signaling in ascending TAAs from Marfan syndrome patients has stimulated an interest in this intracellular signaling pathway. However, paradoxical discoveries have implicated both enhanced TGF-beta signaling and loss of function TGF-beta receptor mutations, in aneurysm formation; obfuscating a clear functional role for TGF-beta in aneurysm development. In an effort to elucidate this subject, TGF-beta signaling and its role in vascular remodeling and pathology will be reviewed, with the aim of identifying potential mechanisms of how TGF-beta signaling may contribute to the formation and progression of TAA.
Figures



References
-
- Liapis CD, Paraskevas KI. The pivotal role of matrix metalloproteinases in the development of human abdominal aortic aneurysms. Vasc Med. 2003;8:267–271. - PubMed
-
- Thompson RW, Geraghty PJ, Lee JK. Abdominal aortic aneurysms: basic mechanisms and clinical implications. Curr Probl Surg. 2002;39:110–230. - PubMed
-
- Isselbacher EM. Thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysms. Circulation. 2005;111:816–828. - PubMed
-
- Thompson RW. Reflections on the pathogenesis of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;10:389–394. - PubMed
-
- Tamarina NA, McMillan WD, Shively VP, Pearce WH. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in aneurysms and normal aorta. Surgery. 1997;122:264–271. discussion 271-262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

