A competitive complex formation mechanism underlies trichome patterning on Arabidopsis leaves
- PMID: 18766177
- PMCID: PMC2564731
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2008.54
A competitive complex formation mechanism underlies trichome patterning on Arabidopsis leaves
Abstract
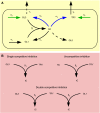
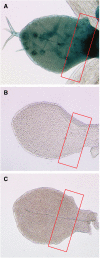
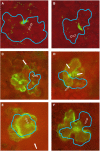
Trichome patterning in Arabidopsis serves as a model system for de novo pattern formation in plants. It is thought to typify the theoretical activator-inhibitor mechanism, although this hypothesis has never been challenged by a combined experimental and theoretical approach. By integrating the key genetic and molecular data of the trichome patterning system, we developed a new theoretical model that allows the direct testing of the effect of experimental interventions and in the prediction of patterning phenotypes. We show experimentally that the trichome inhibitor TRIPTYCHON is transcriptionally activated by the known positive regulators GLABRA1 and GLABRA3. Further, we demonstrate by particle bombardment of protein fusions with GFP that TRIPTYCHON and CAPRICE but not GLABRA1 and GLABRA3 can move between cells. Finally, theoretical considerations suggest promoter swapping and basal overexpression experiments by means of which we are able to discriminate three biologically meaningful variants of the trichome patterning model. Our study demonstrates that the mutual interplay between theory and experiment can reveal a new level of understanding of how biochemical mechanisms can drive biological patterning processes.
Figures
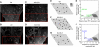
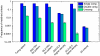
References
-
- Baudry A, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2006) TT8 controls its own expression in a feedback regulation involving TTG1 and homologous MYB and bHLH factors, allowing a strong and cell-specific accumulation of flavonoids in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 46: 768–779 - PubMed
-
- Berger F, Haseloff J, Schiefelbein J, Dolan L (1998) Positional information in root epidermis is defined during embryogenesis and acts in domains with strict boundaries. Curr Biol 8: 421–430 - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt C, Zhao M, Gonzalez A, Lloyd A, Schiefelbein J (2005) The bHLH genes GL3 and EGL3 participate in an intercellular regulatory circuit that controls cell patterning in the Arabidopsis root epidermis. Development 132: 291–298 - PubMed
-
- Clough S, Bent A (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16: 735–743 - PubMed
-
- Cooke J, Zeeman EC (1976) A clock and wavefront model for control of the number of repeated structures during animal morphogenesis. J Theor Biol 58: 455–476 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

