E-cadherin dis-engagement activates the Rap1 GTPase
- PMID: 18767072
- PMCID: PMC2657844
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.21902
E-cadherin dis-engagement activates the Rap1 GTPase
Abstract
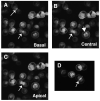
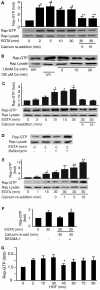
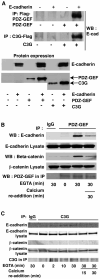
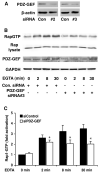
E-cadherin based adherens junctions are finely regulated by multiple cellular signaling events. Here we show that the Ras-related Rap1 GTPase is enriched in regions of nascent cell-cell contacts and strengthens E-cadherin junctions: constitutively active Rap1 expressing MDCK cells exhibit increased junctional contact and resisted calcium depletion-induced cell-cell junction disruption. E-cadherin disengagement activated Rap1 and this correlated with E-cadherin association with the Rap GEFs, C3G and PDZ-GEF I. PDZ-GEF I associated with E-cadherin and beta-catenin whereas C3G interaction with E-cadherin did not involve beta-catenin. Knockdown of PDZ-GEF I in MDCK cells decreased Rap1 activity following E-cadherin junction disruption. We hereby show that Rap1 plays a role in the maintenance and repair of E-cadherin junctions and is activated via an "outside-in" signaling pathway initiated by E-cadherin and mediated at least in part by PDZ-GEF I.
Figures

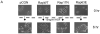
References
-
- Arthur WT, Noren NK, Burridge K. Regulation of Rho family GTPases by cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion. Biol Res. 2002;35:239–46. - PubMed
-
- Balzac F, Avolio M, Degani S, Kaverina I, Torti M, Silengo L, Small JV, Retta SF. E-cadherin endocytosis regulates the activity of Rap1: a traffic light GTPase at the crossroads between cadherin and integrin function. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:4765–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

