Complex events initiated by individual spikes in the human cerebral cortex
- PMID: 18767905
- PMCID: PMC2528052
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060222
Complex events initiated by individual spikes in the human cerebral cortex
Abstract
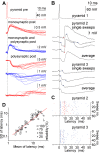
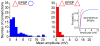
Synaptic interactions between neurons of the human cerebral cortex were not directly studied to date. We recorded the first dataset, to our knowledge, on the synaptic effect of identified human pyramidal cells on various types of postsynaptic neurons and reveal complex events triggered by individual action potentials in the human neocortical network. Brain slices were prepared from nonpathological samples of cortex that had to be removed for the surgical treatment of brain areas beneath association cortices of 58 patients aged 18 to 73 y. Simultaneous triple and quadruple whole-cell patch clamp recordings were performed testing mono- and polysynaptic potentials in target neurons following a single action potential fired by layer 2/3 pyramidal cells, and the temporal structure of events and underlying mechanisms were analyzed. In addition to monosynaptic postsynaptic potentials, individual action potentials in presynaptic pyramidal cells initiated long-lasting (37 +/- 17 ms) sequences of events in the network lasting an order of magnitude longer than detected previously in other species. These event series were composed of specifically alternating glutamatergic and GABAergic postsynaptic potentials and required selective spike-to-spike coupling from pyramidal cells to GABAergic interneurons producing concomitant inhibitory as well as excitatory feed-forward action of GABA. Single action potentials of human neurons are sufficient to recruit Hebbian-like neuronal assemblies that are proposed to participate in cognitive processes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Specialized inhibitory synaptic actions between nearby neocortical pyramidal neurons.Science. 2007 May 4;316(5825):758-61. doi: 10.1126/science.1135468. Science. 2007. PMID: 17478724
-
Limbic gamma rhythms. II. Synaptic and intrinsic mechanisms underlying spike doublets in oscillating subicular neurons.J Neurophysiol. 1998 Jul;80(1):162-71. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.80.1.162. J Neurophysiol. 1998. PMID: 9658038
-
Spontaneous release of GABA activates GABAB receptors and controls network activity in the neonatal rat hippocampus.J Neurophysiol. 1996 Aug;76(2):1036-46. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.76.2.1036. J Neurophysiol. 1996. PMID: 8871218
-
Fluoxetine (prozac) and serotonin act on excitatory synaptic transmission to suppress single layer 2/3 pyramidal neuron-triggered cell assemblies in the human prefrontal cortex.J Neurosci. 2012 Nov 14;32(46):16369-78. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2618-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23152619 Free PMC article.
-
Action potential initiation and propagation in rat neocortical pyramidal neurons.J Physiol. 1997 Dec 15;505 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):617-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.617ba.x. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9457640 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
LRRC37B is a human modifier of voltage-gated sodium channels and axon excitability in cortical neurons.Cell. 2023 Dec 21;186(26):5766-5783.e25. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.11.028. Cell. 2023. PMID: 38134874 Free PMC article.
-
Remodeling of the axon initial segment after focal cortical and white matter stroke.Stroke. 2013 Jan;44(1):182-9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.668749. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Stroke. 2013. PMID: 23233385 Free PMC article.
-
Local connectivity and synaptic dynamics in mouse and human neocortex.Science. 2022 Mar 11;375(6585):eabj5861. doi: 10.1126/science.abj5861. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Science. 2022. PMID: 35271334 Free PMC article.
-
HCN channels at the cell soma ensure the rapid electrical reactivity of fast-spiking interneurons in human neocortex.PLoS Biol. 2023 Feb 6;21(2):e3002001. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002001. eCollection 2023 Feb. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 36745683 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental mechanisms underlying the evolution of human cortical circuits.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2023 Apr;24(4):213-232. doi: 10.1038/s41583-023-00675-z. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36792753 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thomson AM, Radpour S. Excitatory connections between CA1 pyramidal cells revealed by spike triggered averaging in slices of rat hippocampus are partially NMDA receptor mediated. Eur J Neurosci. 1991;3:587–601. - PubMed
-
- Buhl EH, Halasy K, Somogyi P. Diverse sources of hippocampal unitary inhibitory postsynaptic potentials and the number of synaptic release sites. Nature. 1994;368:823–828. - PubMed
-
- Markram H, Lubke J, Frotscher M, Sakmann B. Regulation of synaptic efficacy by coincidence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs. Science. 1997;275:213–215. - PubMed
-
- Povysheva NV, Gonzalez-Burgos G, Zaitsev AV, Kroner S, Barrionuevo G, et al. Properties of excitatory synaptic responses in fast-spiking interneurons and pyramidal cells from monkey and rat prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2006;16:541–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

