Midbrain dopamine neurons: projection target determines action potential duration and dopamine D(2) receptor inhibition
- PMID: 18768684
- PMCID: PMC6670880
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1526-08.2008
Midbrain dopamine neurons: projection target determines action potential duration and dopamine D(2) receptor inhibition
Abstract
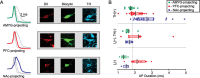
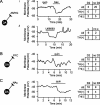
Broad action potentials (APs) and dopamine (DA) D(2) receptor (D(2)R)-mediated inhibition are widely used to identify midbrain DA neurons. However, when these measures are taken alone they do not predict DA content in ventral tegmental area (VTA) neurons. In fact, some VTA neuronal properties correlate better with projection target than neurotransmitter content. Here we report that amygdala (AMYG)-projecting VTA DA neurons have brief APs and lack D(2)R agonist (quinpirole; 1 microM) autoinhibition. However, they are hyperpolarized by both the GABA(B) agonist baclofen (1 microM) and the kappa-opioid receptor agonist U69593 [(+)-(5alpha,7alpha,8beta)-N-methyl-N-[7-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-1-oxaspiro[4.5]dec-8-yl]benzeneacetamide; 1 microM]. Furthermore, we show that accurate prediction of DA content in VTA neurons is possible when the projection target is known: in both nucleus accumbens- and AMYG-projecting neural populations, AP durations are significantly longer in DA than non-DA neurons. Among prefrontal cortex-projecting neurons, quinpirole sensitivity, but not AP duration, is a predictor of DA content. Therefore, in the VTA, AP duration and inhibition by D(2)R agonists may be valid markers of DA content in neurons of known projection target.
Figures


References
-
- Aghajanian GK, Bunney BS. Pharmacological characterization of dopamine “autoreceptors” by microiontophoretic single-cell recording studies. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1977;16:433–438. - PubMed
-
- Alderson HL, Latimer MP, Winn P. Intravenous self-administration of nicotine is altered by lesions of the posterior, but not anterior, pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;23:2169–2175. - PubMed
-
- Bunney BS, Walters JR, Roth RH, Aghajanian GK. Dopaminergic neurons: effect of antipsychotic drugs and amphetamine on single cell activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973a;185:560–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
