Contrasting responses of lymphoid progenitors to canonical and noncanonical Wnt signals
- PMID: 18768850
- PMCID: PMC2562264
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.6.3955
Contrasting responses of lymphoid progenitors to canonical and noncanonical Wnt signals
Abstract
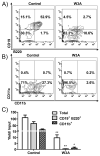
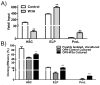
The Wnt family of secreted glycoproteins has been implicated in many aspects of development, but its contribution to blood cell formation is controversial. We overexpressed Wnt3a, Wnt5a, and Dickkopf 1 in stromal cells from osteopetrotic mice and used them in coculture experiments with highly enriched stem and progenitor cells. The objective was to learn whether and how particular stages of B lymphopoiesis are responsive to these Wnt family ligands. We found that canonical Wnt signaling, through Wnt3a, inhibited B and plasmacytoid dendritic cell, but not conventional dendritic cell development. Wnt5a, which can oppose canonical signaling or act through a different pathway, increased B lymphopoiesis. Responsiveness to both Wnt ligands diminished with time in culture and stage of development. That is, only hematopoietic stem cells and very primitive progenitors were affected. Although Wnt3a promoted retention of hematopoietic stem cell markers, cell yields and dye dilution experiments indicated it was not a growth stimulus. Other results suggest that lineage instability results from canonical Wnt signaling. Lymphoid progenitors rapidly down-regulated RAG-1, and some acquired stem cell-staining characteristics as well as myeloid and erythroid potential when exposed to Wnt3a-producing stromal cells. We conclude that at least two Wnt ligands can differentially regulate early events in B lymphopoiesis, affecting entry and progression in distinct differentiation lineages.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Active form of Notch members can enforce T lymphopoiesis on lymphoid progenitors in the monolayer culture specific for B cell development.J Immunol. 2003 May 15;170(10):4973-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.10.4973. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12734340
-
Molecular dissection of prethymic progenitor entry into the T lymphocyte developmental pathway.J Immunol. 2007 Jul 1;179(1):421-38. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.1.421. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17579063
-
Wnt5a inhibits canonical Wnt signaling in hematopoietic stem cells and enhances repopulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Sep 25;104(39):15436-41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704747104. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17881570 Free PMC article.
-
Life before the pre-B cell receptor checkpoint: specification and commitment of primitive lymphoid progenitors in adult bone marrow.Semin Immunol. 2006 Feb;18(1):2-11. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2005.10.005. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Semin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16310376 Review.
-
Plugging the leaky pre-B cell receptor.J Immunol. 2010 Feb 1;184(3):1127-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0990113. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20089707 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
WNT3A promotes hematopoietic or mesenchymal differentiation from hESCs depending on the time of exposure.Stem Cell Reports. 2013 Jun 4;1(1):53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2013.04.002. eCollection 2013. Stem Cell Reports. 2013. PMID: 24052942 Free PMC article.
-
B-1 cells and B-1 cell precursors prompt different responses to Wnt signaling.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 21;13(6):e0199332. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199332. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29928002 Free PMC article.
-
Kallistatin Attenuates Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis by Inhibiting Activation of T Cells.Front Immunol. 2020 May 21;11:975. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00975. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32508841 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical Wnt signaling in megakaryocytes regulates proplatelet formation.Blood. 2013 Jan 3;121(1):188-96. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-03-416875. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23160460 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt5a does not support hematopoiesis in stroma-free, serum-free cultures.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53669. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053669. Epub 2013 Jan 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23341970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austin TW, Solar GP, Ziegler FC, Liem L, Matthews W. A role for the Wnt gene family in hematopoiesis: expansion of multilineage progenitor cells. Blood. 1997;89:3624–3635. - PubMed
-
- Van Den Berg DJ, Sharma AK, Bruno E, Hoffman R. Role of members of the Wnt gene family in human hematopoiesis. Blood. 1998;92:3189–3202. - PubMed
-
- Sato N, Meijer L, Skaltsounis L, Greengard P, Brivanlou AH. Maintenance of pluripotency in human and mouse embryonic stem cells through activation of Wnt signaling by a pharmacological GSK-3-specific inhibitor. Nat Med. 2004;10:55–63. - PubMed
-
- Willert K, Brown JD, Danenberg E, Duncan AW, Weissman IL, Reya T, Yates JR, III, Nusse R. Wnt proteins are lipid-modified and can act as stem cell growth factors. Nature. 2003;423:448–452. - PubMed
-
- Reya T, Duncan AW, Ailles L, Domen J, Scherer DC, Willert K, Hintz L, Nusse R, Weissman IL. A role for Wnt signalling in self-renewal of haematopoietic stem cells. Nature. 2003;423:409–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

