TH17 cells mediate steroid-resistant airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in mice
- PMID: 18768865
- PMCID: PMC3638757
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.6.4089
TH17 cells mediate steroid-resistant airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in mice
Abstract
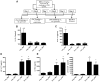
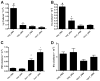
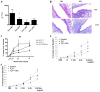
Steroid-resistant asthma comprises an important source of morbidity in patient populations. T(H)17 cells represent a distinct population of CD4(+) Th cells that mediate neutrophilic inflammation and are characterized by the production of IL-17, IL-22, and IL-6. To investigate the function of T(H)17 cells in the context of Ag-induced airway inflammation, we polarized naive CD4(+) T cells from DO11.10 OVA-specific TCR-transgenic mice to a T(H)2 or T(H)17 phenotype by culturing in conditioned medium. In addition, we also tested the steroid responsiveness of T(H)2 and T(H)17 cells. In vitro, T(H)17 cytokine responses were not sensitive to dexamethasone (DEX) treatment despite immunocytochemistry confirming glucocorticoid receptor translocation to the nucleus following treatment. Transfer of T(H)2 cells to mice challenged with OVA protein resulted in lymphocyte and eosinophil emigration into the lung that was markedly reduced by DEX treatment, whereas T(H)17 transfer resulted in increased CXC chemokine secretion and neutrophil influx that was not attenuated by DEX. Transfer of T(H)17 or T(H)2 cells was sufficient to induce airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) to methacholine. Interestingly, AHR was not attenuated by DEX in the T(H)17 group. These data demonstrate that polarized Ag-specific T cells result in specific lung pathologies. Both T(H)2 and T(H)17 cells are able to induce AHR, whereas T(H)17 cell-mediated airway inflammation and AHR are steroid resistant, indicating a potential role for T(H)17 cells in steroid-resistant asthma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures

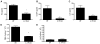
References
-
- Wallen N, Kita H, Weiler D, Gleich GJ. Glucocorticoids inhibit cytokine-mediated eosinophil survival. J Immunol. 1991;147:3490–3495. - PubMed
-
- Lamas AM, Leon OG, Schleimer RP. Glucocorticoids inhibit eosinophil responses to granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1991;147:254–259. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ. Distribution of receptor targets in the lung. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2004;1:345–351. - PubMed
-
- Weaver CT, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Harrington LE. IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:821–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

