A gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-independent pathway of glutathione catabolism to glutamate via 5-oxoproline in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 18768907
- PMCID: PMC2577253
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.108.125716
A gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-independent pathway of glutathione catabolism to glutamate via 5-oxoproline in Arabidopsis
Abstract
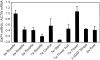
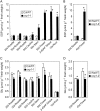
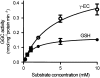
The degradation pathway of glutathione (GSH) in plants is not well understood. In mammals, GSH is predominantly metabolized through the gamma-glutamyl cycle, where GSH is degraded by the sequential reaction of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), gamma-glutamyl cyclotransferase, and 5-oxoprolinase to yield glutamate (Glu) and dipeptides that are subject to peptidase action. In this study, we examined if GSH is degraded through the same pathway in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) as occurs in mammals. In Arabidopsis, the oxoprolinase knockout mutants (oxp1-1 and oxp1-2) accumulate more 5-oxoproline (5OP) and less Glu than wild-type plants, suggesting substantial metabolite flux though 5OP and that 5OP is a major contributor to Glu steady-state levels. In the ggt1-1/ggt4-1/oxp1-1 triple mutant with no GGT activity in any organs except young siliques, the 5OP concentration in leaves was not different from that in oxp1-1, suggesting that GGTs are not major contributors to 5OP production in Arabidopsis. 5OP formation strongly tracked the level of GSH in Arabidopsis plants, suggesting that GSH is the precursor of 5OP in a GGT-independent reaction. Kinetics analysis suggests that gamma-glutamyl cyclotransferase is the major source of GSH degradation and 5OP formation in Arabidopsis. This discovery led us to propose a new pathway for GSH turnover in plants where GSH is converted to 5OP and then to Glu by the combined action of gamma-glutamyl cyclotransferase and 5-oxoprolinase in the cytoplasm.
Figures


References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657 - PubMed
-
- An YQ, McDowell JM, Huang SR, McKinney EC, Chambliss S, Meagher RB (1996) Strong, constitutive expression of the Arabidopsis ACT2/ACT8 actin subclass in vegetative tissues. Plant J 10 107–121 - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72 248–254 - PubMed
-
- Beck A, Lendzian K, Oven M, Christmann A, Grill E (2003) Phytochelatin synthase catalyzes key step in turnover of glutathione conjugates. Phytochemistry 62 423–431 - PubMed
-
- Blum R, Beck A, Korte A, Stenge A, Letzel T, Lendzian K, Grill E (2007) Function of phytochelatin synthase in catabolism of glutathione-conjugates. Plant J 49 740–749 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

