Resolving individuals contributing trace amounts of DNA to highly complex mixtures using high-density SNP genotyping microarrays
- PMID: 18769715
- PMCID: PMC2516199
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000167
Resolving individuals contributing trace amounts of DNA to highly complex mixtures using high-density SNP genotyping microarrays
Abstract
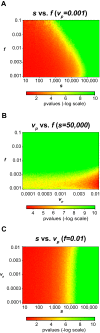
We use high-density single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotyping microarrays to demonstrate the ability to accurately and robustly determine whether individuals are in a complex genomic DNA mixture. We first develop a theoretical framework for detecting an individual's presence within a mixture, then show, through simulations, the limits associated with our method, and finally demonstrate experimentally the identification of the presence of genomic DNA of specific individuals within a series of highly complex genomic mixtures, including mixtures where an individual contributes less than 0.1% of the total genomic DNA. These findings shift the perceived utility of SNPs for identifying individual trace contributors within a forensics mixture, and suggest future research efforts into assessing the viability of previously sub-optimal DNA sources due to sample contamination. These findings also suggest that composite statistics across cohorts, such as allele frequency or genotype counts, do not mask identity within genome-wide association studies. The implications of these findings are discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Comment in
-
Public access to genome-wide data: five views on balancing research with privacy and protection.PLoS Genet. 2009 Oct;5(10):e1000665. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000665. Epub 2009 Oct 2. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19798440 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Egeland T, Dalen I, Mostad PF. Estimating the number of contributors to a DNA profile. Int J Legal Med. 2003;117:271–275. - PubMed
-
- Hu YQ, Fung WK. Interpreting DNA mixtures with the presence of relatives. Int J Legal Med. 2003;117:39–45. - PubMed
-
- Balding DJ. Likelihood-based inference for genetic correlation coefficients. Theor Popul Biol. 2003;63:221–230. - PubMed
-
- Clayton TM, Whitaker JP, Sparkes R, Gill P. Analysis and interpretation of mixed forensic stains using DNA STR profiling. Forensic Sci Int. 1998;91:55–70. - PubMed
-
- Cowell RG, Lauritzen SL, Mortera J. Identification and separation of DNA mixtures using peak area information. Forensic Sci Int. 2007;166:28–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

