Network inference algorithms elucidate Nrf2 regulation of mouse lung oxidative stress
- PMID: 18769717
- PMCID: PMC2516606
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000166
Network inference algorithms elucidate Nrf2 regulation of mouse lung oxidative stress
Abstract
A variety of cardiovascular, neurological, and neoplastic conditions have been associated with oxidative stress, i.e., conditions under which levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) are elevated over significant periods. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) regulates the transcription of several gene products involved in the protective response to oxidative stress. The transcriptional regulatory and signaling relationships linking gene products involved in the response to oxidative stress are, currently, only partially resolved. Microarray data constitute RNA abundance measures representing gene expression patterns. In some cases, these patterns can identify the molecular interactions of gene products. They can be, in effect, proxies for protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions. Traditional techniques used for clustering coregulated genes on high-throughput gene arrays are rarely capable of distinguishing between direct transcriptional regulatory interactions and indirect ones. In this study, newly developed information-theoretic algorithms that employ the concept of mutual information were used: the Algorithm for the Reconstruction of Accurate Cellular Networks (ARACNE), and Context Likelihood of Relatedness (CLR). These algorithms captured dependencies in the gene expression profiles of the mouse lung, allowing the regulatory effect of Nrf2 in response to oxidative stress to be determined more precisely. In addition, a characterization of promoter sequences of Nrf2 regulatory targets was conducted using a Support Vector Machine classification algorithm to corroborate ARACNE and CLR predictions. Inferred networks were analyzed, compared, and integrated using the Collective Analysis of Biological Interaction Networks (CABIN) plug-in of Cytoscape. Using the two network inference algorithms and one machine learning algorithm, a number of both previously known and novel targets of Nrf2 transcriptional activation were identified. Genes predicted as novel Nrf2 targets include Atf1, Srxn1, Prnp, Sod2, Als2, Nfkbib, and Ppp1r15b. Furthermore, microarray and quantitative RT-PCR experiments following cigarette-smoke-induced oxidative stress in Nrf2(+/+) and Nrf2(-/-) mouse lung affirmed many of the predictions made. Several new potential feed-forward regulatory loops involving Nrf2, Nqo1, Srxn1, Prdx1, Als2, Atf1, Sod1, and Park7 were predicted. This work shows the promise of network inference algorithms operating on high-throughput gene expression data in identifying transcriptional regulatory and other signaling relationships implicated in mammalian disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

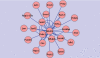
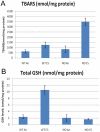




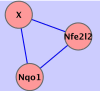



Similar articles
-
Nrf2-dependent sulfiredoxin-1 expression protects against cigarette smoke-induced oxidative stress in lungs.Free Radic Biol Med. 2009 Feb 1;46(3):376-86. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.10.026. Epub 2008 Nov 1. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009. PMID: 19027064 Free PMC article.
-
ARACNE: an algorithm for the reconstruction of gene regulatory networks in a mammalian cellular context.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Mar 20;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-S1-S7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16723010 Free PMC article.
-
TimeDelay-ARACNE: Reverse engineering of gene networks from time-course data by an information theoretic approach.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Mar 25;11:154. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-154. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20338053 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Network Inference and analysis using SEBINI and CABIN.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;541:551-76. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-243-4_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19381531 Review.
-
Nrf2 protects against airway disorders.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010 Apr 1;244(1):43-56. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.07.024. Epub 2009 Jul 29. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19646463 Review.
Cited by
-
Prediction and redesign of protein-protein interactions.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2014 Nov-Dec;116(2-3):194-202. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2014.05.004. Epub 2014 May 27. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24878423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JUNB is a key transcriptional modulator of macrophage activation.J Immunol. 2015 Jan 1;194(1):177-86. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401595. Epub 2014 Dec 3. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25472994 Free PMC article.
-
Early events in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Smoking-induced reprogramming of airway epithelial basal progenitor cells.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014 Dec;11 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S252-8. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201402-049AW. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014. PMID: 25525728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α-phosphatase (CreP/PPP1R15B) regulates membrane traffic.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 12;287(42):35299-35317. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.379883. Epub 2012 Aug 22. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22915583 Free PMC article.
-
Dimethyl Fumarate Protects Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells and Neurons from Oxidative Damage through Nrf2-ERK1/2 MAPK Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jun 17;16(6):13885-907. doi: 10.3390/ijms160613885. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26090715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Droge W. Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:47–95. - PubMed
-
- Jaiswal AK. Antioxidant response element. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994;48:439–444. - PubMed
-
- Chen XL, Kunch C. Induction of cytoprotective genes through Nrf2/antioxidant response element pathway: a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10:879–891. - PubMed
-
- Venugopal R, Jaiswal AK. Nrf2 and Nrf1 in association with Jun proteins regulate antioxidant response element-mediated expression and coordinated induction of genes encoding detoxifying enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:14960–14965. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

