Yersinia enterocolitica serum resistance proteins YadA and ail bind the complement regulator C4b-binding protein
- PMID: 18769718
- PMCID: PMC2516929
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000140
Yersinia enterocolitica serum resistance proteins YadA and ail bind the complement regulator C4b-binding protein
Abstract
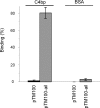
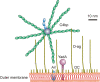
Many pathogens are equipped with factors providing resistance against the bactericidal action of complement. Yersinia enterocolitica, a Gram-negative enteric pathogen with invasive properties, efficiently resists the deleterious action of human complement. The major Y. enterocolitica serum resistance determinants include outer membrane proteins YadA and Ail. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) O-antigen (O-ag) and outer core (OC) do not contribute directly to complement resistance. The aim of this study was to analyze a possible mechanism whereby Y. enterocolitica could inhibit the antibody-mediated classical pathway of complement activation. We show that Y. enterocolitica serotypes O:3, O:8, and O:9 bind C4b-binding protein (C4bp), an inhibitor of both the classical and lectin pathways of complement. To identify the C4bp receptors on Y. enterocolitica serotype O:3 surface, a set of mutants expressing YadA, Ail, O-ag, and OC in different combinations was tested for the ability to bind C4bp. The studies showed that both YadA and Ail acted as C4bp receptors. Ail-mediated C4bp binding, however, was blocked by the O-ag and OC, and could be observed only with mutants lacking these LPS structures. C4bp bound to Y. enterocolitica was functionally active and participated in the factor I-mediated degradation of C4b. These findings show that Y. enterocolitica uses two proteins, YadA and Ail, to bind C4bp. Binding of C4bp could help Y. enterocolitica to evade complement-mediated clearance in the human host.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




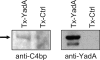

Similar articles
-
Functional recruitment of the human complement inhibitor C4BP to Yersinia pseudotuberculosis outer membrane protein Ail.J Immunol. 2012 May 1;188(9):4450-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103149. Epub 2012 Mar 30. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22467648
-
Functional mapping of YadA- and Ail-mediated binding of human factor H to Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3.Infect Immun. 2008 Nov;76(11):5016-27. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00314-08. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18765735 Free PMC article.
-
Role of YadA, Ail, and Lipopolysaccharide in Serum Resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica Serotype O:3.Infect Immun. 2005 Apr;73(4):2232-44. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.4.2232-2244.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15784567 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial cell surface structures in Yersinia enterocolitica.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2012 Jun;60(3):199-209. doi: 10.1007/s00005-012-0168-z. Epub 2012 Apr 8. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2012. PMID: 22484801 Review.
-
Interactions between Yersinia enterocolitica and the host with special reference to virulence plasmid encoded adhesion and humoral immunity.Dan Med Bull. 1992 Apr;39(2):155-72. Dan Med Bull. 1992. PMID: 1611921 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome Scale Analysis Reveals IscR Directly and Indirectly Regulates Virulence Factor Genes in Pathogenic Yersinia.mBio. 2021 Jun 29;12(3):e0063321. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00633-21. Epub 2021 Jun 1. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34060331 Free PMC article.
-
Association of complement receptor 2 polymorphisms with innate resistance to HIV-1 infection.Genes Immun. 2015 Mar;16(2):134-41. doi: 10.1038/gene.2014.71. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Genes Immun. 2015. PMID: 25569262
-
Functional characterization of LcpA, a surface-exposed protein of Leptospira spp. that binds the human complement regulator C4BP.Infect Immun. 2010 Jul;78(7):3207-16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00279-10. Epub 2010 Apr 19. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20404075 Free PMC article.
-
Ail binding to fibronectin facilitates Yersinia pestis binding to host cells and Yop delivery.Infect Immun. 2010 Aug;78(8):3358-68. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00238-10. Epub 2010 May 24. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20498264 Free PMC article.
-
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, Samonella, Shigella and Yersinia: cellular aspects of host-bacteria interactions in enteric diseases.Gut Pathog. 2010 Jul 22;2(1):8. doi: 10.1186/1757-4749-2-8. Gut Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20649986 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

