The social brain: neural basis of social knowledge
- PMID: 18771388
- PMCID: PMC2588649
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.psych.60.110707.163514
The social brain: neural basis of social knowledge
Abstract
Social cognition in humans is distinguished by psychological processes that allow us to make inferences about what is going on inside other people-their intentions, feelings, and thoughts. Some of these processes likely account for aspects of human social behavior that are unique, such as our culture and civilization. Most schemes divide social information processing into those processes that are relatively automatic and driven by the stimuli, versus those that are more deliberative and controlled, and sensitive to context and strategy. These distinctions are reflected in the neural structures that underlie social cognition, where there is a recent wealth of data primarily from functional neuroimaging. Here I provide a broad survey of the key abilities, processes, and ways in which to relate these to data from cognitive neuroscience.
Figures

References
-
- Adams RB, Kleck RE. Perceived gaze direction and the processing of facial displays of emotion. Psychol Sci. 2003;14:644–47. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R. Cognitive neuroscience of human social behavior. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:165–78. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R. How do we know the minds of others? Domain-specificity, simulation, and enactive social cognition. Brain Res. 2006;1079:25–35. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R, Gosselin F, Buchanan TW, Tranel D, Schyns P, Damasio AR. A mechanism for impaired fear recognition after amygdala damage. Nature. 2005;433:68–72. - PubMed
-
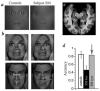
This study found that a patient with bilateral amygdala lesions was impaired in recognizing fear in facial expressions because patient failed to fixate the eyes in faces and thus failed to use facial information normally needed to recognize fear.
-
- Adolphs R, Spezio M. The neuroscience of social cognition. In: Cacioppo JT, Berntson G, editors. Handbook of Neuroscience for the Behavioral Sciences. New York: Wiley; 2008. In press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

