Population pharmacokinetic analysis for risperidone using highly sparse sampling measurements from the CATIE study
- PMID: 18771484
- PMCID: PMC2661978
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03276.x
Population pharmacokinetic analysis for risperidone using highly sparse sampling measurements from the CATIE study
Abstract
Aims: To characterize pharmacokinetic (PK) variability of risperidone and 9-OH risperidone using sparse sampling and to evaluate the effect of covariates on PK parameters.
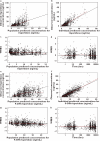
Methods: PK analysis used plasma samples collected from the Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness. A nonlinear mixed-effects model was developed using NONMEM to describe simultaneously the risperidone and 9-OH risperidone concentration-time profile. Covariate effects on risperidone and 9-OH risperidone PK parameters were assessed, including age, weight, sex, smoking status, race and concomitant medications.
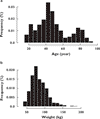
Results: PK samples comprised 1236 risperidone and 1236 9-OH risperidone concentrations from 490 subjects that were available for analysis. Ages ranged from 18 to 93 years. Population PK submodels for both risperidone and 9-OH risperidone with first-order absorption were selected to describe the concentration-time profile of risperidone and 9-OH risperidone. A mixture model was incorporated with risperidone clearance (CL) separately estimated for three subpopulations [poor metabolizer (PM), extensive metabolizer (EM) and intermediate metabolizer (IM)]. Age significantly affected 9-OH risperidone clearance. Population parameter estimates for CL in PM, IM and EM were 12.9, 36 and 65.4 l h(-1) and parameter estimates for risperidone half-life in PM, IM and EM were 25, 8.5 and 4.7 h, respectively.
Conclusions: A one-compartment mixture model with first-order absorption adequately described the risperidone and 9-OH risperidone concentrations. Age was identified as a significant covariate on 9-OH risperidone clearance in this study.
Figures




References
-
- Spina E, Avenoso A, Facciola G, Salemi M, Scordo MG, Ancione M, Madia AG, Perucca E. Relationship between plasma risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone concentrations and clinical response in patients with schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2001;153:238–43. - PubMed
-
- Chouinard G, Arnott W. Clinical review of risperidone. Can J Psychiatry. 1993;38(Suppl 3):S89–95. - PubMed
-
- Leysen JE, Gommeren W, Eens A, de Chaffoy de Courcelles D, Stoof JC, Janssen PA. Biochemical profile of risperidone, a new antipsychotic. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988;247:661–70. - PubMed
-
- Aichhorn W, Weiss U, Marksteiner J, Kemmler G, Walch T, Zernig G, Stelzig-Schoeler R, Stuppaeck C, Geretsegger C. Influence of age and gender on risperidone plasma concentrations. J Psychopharmacol. 2005;19:395–401. - PubMed
-
- Snoeck E, Van Peer A, Sack M, Horton M, Mannens G, Woestenborghs R, Meibach R, Heykants J. Influence of age, renal and liver impairment on the pharmacokinetics of risperidone in man. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1995;122:223–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

