Modulation of the cortical processing of novel and target stimuli by drugs affecting glutamate and GABA neurotransmission
- PMID: 18771605
- PMCID: PMC2900256
- DOI: 10.1017/S1461145708009334
Modulation of the cortical processing of novel and target stimuli by drugs affecting glutamate and GABA neurotransmission
Abstract
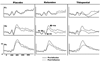
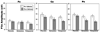
In this double-blind, placebo-controlled study, we examined the effects of subanaesthetic doses of ketamine (an NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist) and thiopental (a GABA-A receptor agonist) on the event-related potential (ERP) correlates of deviant stimulus processing in 24 healthy adults. Participants completed three separate pharmacological challenge sessions (ketamine, thiopental, saline) in a counterbalanced order. EEG data were recorded both before and during each challenge while participants performed a visual 'oddball' task consisting of infrequent 'target' and 'novel' stimuli intermixed with frequent 'standard' stimuli. We examined drug effects on the amplitude and latency of the P300 (P3) component of the ERP elicited by target (P3b) and novel stimuli (P3a), as well as the N200 (N2) component elicited by both target and novel stimuli, and the N100 (N1) elicited by standard stimuli. Relative to placebo, both drugs reduced the amplitude of parietal P3b. While both drugs reduced parietal P3a and Novelty N2, ketamine also shortened P3a latency, reduced Novelty N2 amplitude more than thiopental, and increased frontal P3a amplitude relative to placebo. Overall, the data suggest that both the GABA-A and NMDA receptor systems modulate P3b and P3a. NMDA antagonism appears to lead to more varied effects on the neural correlates of novelty processing.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ethanol-like effects of thiopental and ketamine in healthy humans.J Psychopharmacol. 2010 Feb;24(2):203-11. doi: 10.1177/0269881108098612. Epub 2008 Nov 21. J Psychopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19028835 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dose-related modulation of event-related potentials to novel and target stimuli by intravenous Δ⁹-THC in humans.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 Jun;37(7):1632-46. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.8. Epub 2012 Feb 15. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22334121 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Event-related potential study of novelty processing abnormalities in autism.Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2009 Mar;34(1):37-51. doi: 10.1007/s10484-009-9074-5. Epub 2009 Feb 6. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2009. PMID: 19199028
-
Updating P300: an integrative theory of P3a and P3b.Clin Neurophysiol. 2007 Oct;118(10):2128-48. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2007.04.019. Epub 2007 Jun 18. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17573239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neurophysiology of P 300--an integrated review.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Apr;19(8):1480-8. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25967724 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurochemistry of Visual Attention.Front Neurosci. 2021 May 5;15:643597. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.643597. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34025339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of nicotine on the neurophysiological and behavioral effects of ketamine in humans.Front Psychiatry. 2014 Jan 24;5:3. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00003. eCollection 2014. Front Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24478731 Free PMC article.
-
A roadmap for development of neuro-oscillations as translational biomarkers for treatment development in neuropsychopharmacology.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020 Aug;45(9):1411-1422. doi: 10.1038/s41386-020-0697-9. Epub 2020 May 6. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32375159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional imaging markers for susceptibility to psychosis.Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Nov;25(11):2773-2785. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0679-7. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Mol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32066828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutamatergic modulation of auditory information processing in the human brain.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Jun 1;71(11):969-77. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.09.031. Epub 2011 Oct 29. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22036036 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ahn KH, Youn T, Cho SS, Ha TH, Ha KS, Kim MS, Kwon JS. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in working memory impairments in schizophrenia: event-related potential study of late stage of working memory process. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003;27(6):993–999. - PubMed
-
- Bekker EM, Kenemans JL, Verbaten MN. Source analysis of the N2 in a cued Go/NoGo task. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2005;22(2):221–231. - PubMed
-
- Bertoli S, Probst R. Lack of standard N2 in elderly participants indicates inhibitory processing deficit. Neuroreport. 2005;16(17):1933–1937. - PubMed
-
- Courchesne E, Hillyard SA, Galambos R. Stimulus novelty, task relevance and the visual evoked potential in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1975;39(2):131–143. - PubMed
-
- Crowley KE, Colrain IM. A review of the evidence for P2 being an independent component process: age, sleep and modality. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004;115(4):732–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

