Androgen and estrogen (alpha) receptor localization on periaqueductal gray neurons projecting to the rostral ventromedial medulla in the male and female rat
- PMID: 18771723
- PMCID: PMC2626772
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2008.08.001
Androgen and estrogen (alpha) receptor localization on periaqueductal gray neurons projecting to the rostral ventromedial medulla in the male and female rat
Abstract
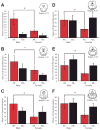
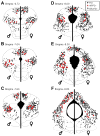
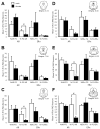
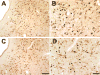
The periaqueductal gray (PAG) is involved in many gonadal steroid-sensitive behaviors, including responsiveness to pain. The PAG projects to the rostral ventromedial medulla (RVM), comprising the primary circuit driving pain inhibition. Morphine administered systemically or directly into the PAG produces greater analgesia in male compared to female rats, while manipulation of gonadal hormones alters morphine potency in both sexes. It is unknown if these alterations are due to steroidal actions on PAG neurons projecting to the RVM. The expression of androgen (AR) and estrogen (ERalpha) receptors in the PAG of female rats and within this descending inhibitory pathway in both sexes is unknown. The present study used immunohistochemical techniques (1) to map the distribution of AR and ERalpha across the rostrocaudal axis of the PAG; and (2) to determine whether AR and/or ERalpha were colocalized on PAG neurons projecting to the RVM in male and female rats. AR and ERalpha immunoreactive neurons (AR-IR, ERalpha-IR) were densely distributed within the caudal PAG of male rats, with the majority localized in the lateral/ventrolateral PAG. Females had significantly fewer AR-IR neurons, while the quantity of ERalpha was comparable between the sexes. In both sexes, approximately 25-50% of AR-IR neurons and 20-50% of ERalpha-IR neurons were retrogradely labeled. This study provides direct evidence of the expression of steroid receptors in the PAG and the descending pathway driving pain inhibition in both male and female rats and may provide a mechanism whereby gonadal steroids modulate pain and morphine potency.
Figures


References
-
- Albert DJ, Jonik RH, Walsh ML. Hormone-dependent aggression in the female rat: testosterone plus estradiol implants prevent the decline in aggression following ovariectomy. Physiol Behav. 1991;49:673–677. - PubMed
-
- Albert DJ, Jonik RH, Watson NV, Gorzalka BB, Walsh ML. Hormone-dependent aggression in male rats is proportional to serum testosterone concentration but sexual behavior is not. Physiol Behav. 1990;48:409–416. - PubMed
-
- Aloisi AM, Ceccarelli I, Fiorenzani P, De Padova AM, Massafra C. Testosterone affects formalin-induced responses differently in male and female rats. Neurosci Lett. 2004;361:262–264. - PubMed
-
- Alper RH, Schmitz TM. Estrogen increases the bradycardia elicited by central administration of the serotonin1A agonist 8-OH-DPAT in conscious rats. Brain Res. 1996;716:224–228. - PubMed
-
- Bandler R, Carrive P. Integrated defence reaction elicited by excitatory amino acid microinjection in the midbrain periaqueductal grey region of the unrestrained cat. Brain Res. 1988;439:95–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

