Full-length Escherichia coli SecA dimerizes in a closed conformation in solution as determined by cryo-electron microscopy
- PMID: 18772144
- PMCID: PMC2570880
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.C800160200
Full-length Escherichia coli SecA dimerizes in a closed conformation in solution as determined by cryo-electron microscopy
Abstract
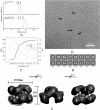
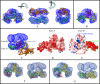
SecA is an obligatory component of the Escherichia coli general secretion pathway. However, the oligomeric structure of SecA and SecA conformational changes during translocation processes are still unclear. Here we obtained the three-dimensional structure of E. coli wild-type full-length SecA in solution by single particle cryo-electron microscopy and determined its oligomeric organization. In this structure, SecA occurs as a dimer in which the two protomers are arranged in an antiparallel mode, with a novel electrostatic interface, and both protomers are in closed conformation. The system developed here may provide a promising technique for studying dynamic structural changes in SecA.
Figures
References
-
- Cabelli, R. J., Chen, L., Tai, P. C., and Oliver, D. B. (1988) Cell 55 683–692 - PubMed
-
- Oliver, D. B., and Beckwith, J. (1981) Cell 25 765–772 - PubMed
-
- Manting, E. H., and Driessen, A. J. (2000) Mol. Microbiol. 37 226–238 - PubMed
-
- Wickner, W., and Leonard, M. R. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271 29514–29516 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

