Brain cholinergic impairment in liver failure
- PMID: 18772221
- PMCID: PMC2577805
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awn209
Brain cholinergic impairment in liver failure
Abstract
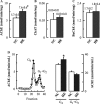
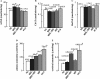
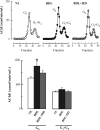
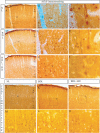
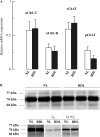
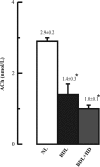
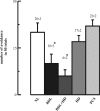
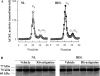
The cholinergic system is involved in specific behavioural responses and cognitive processes. Here, we examined potential alterations in the brain levels of key cholinergic enzymes in cirrhotic patients and animal models with liver failure. An increase (~30%) in the activity of the acetylcholine-hydrolyzing enzyme, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is observed in the brain cortex from patients deceased from hepatic coma, while the activity of the acetylcholine-synthesizing enzyme, choline acetyltransferase, remains unaffected. In agreement with the human data, AChE activity in brain cortical extracts of bile duct ligated (BDL) rats was increased (~20%) compared to controls. A hyperammonemic diet did not result in any further increase of AChE levels in the BDL model, and no change was observed in hyperammonemic diet rats without liver disease. Portacaval shunted rats which display increased levels of cerebral ammonia did not show any brain cholinergic abnormalities, confirming that high ammonia levels do not play a role in brain AChE changes. A selective increase of tetrameric AChE, the major AChE species involved in hydrolysis of acetylcholine in the brain, was detected in both cirrhotic humans and BDL rats. Histological examination of BDL and non-ligated rat brains shows that the subcellular localization of both AChE and choline acetyltransferase, and thus the accessibility to their substrates, appears unaltered by the pathological condition. The BDL-induced increase in AChE activity was not parallelled by an increase in mRNA levels. Increased AChE in BDL cirrhotic rats leads to a pronounced decrease (~50-60%) in the levels of acetylcholine. Finally, we demonstrate that the AChE inhibitor rivastigmine is able to improve memory deficits in BDL rats. One week treatment with rivastigmine (0.6 mg/kg; once a day, orally, for a week) resulted in a 25% of inhibition in the enzymatic activity of AChE with no change in protein composition, as assessed by sucrose density gradient fractionation and western blotting analysis. In conclusion, this study is the first direct evidence of a cholinergic imbalance in the brain as a consequence of liver failure and points to the possible role of the cholinergic system in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rivastigmine antagonizes deficits in prepulse inhibition induced by selective immunolesioning of cholinergic neurons in nucleus basalis magnocellularis.Neuroscience. 2002;114(1):91-8. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00234-8. Neuroscience. 2002. PMID: 12207957
-
Effect of treatment with the cholinesterase inhibitor rivastigmine on vesicular acetylcholine transporter and choline acetyltransferase in rat brain.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2004 May;26(4):363-73. doi: 10.1081/ceh-120034140. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2004. PMID: 15195690
-
Changes in liver and plasma acetylcholinesterase in rats with cirrhosis induced by bile duct ligation.Hepatology. 2006 Mar;43(3):444-53. doi: 10.1002/hep.21071. Hepatology. 2006. PMID: 16496349
-
Clinical pharmacology of rivastigmine: a new-generation acetylcholinesterase inhibitor for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Clin Ther. 1998 Jul-Aug;20(4):634-47. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(98)80127-6. Clin Ther. 1998. PMID: 9737824 Review.
-
Rivastigmine in vascular dementia.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004 Jun;5(6):1399-410. doi: 10.1517/14656566.5.6.1399. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15163283 Review.
Cited by
-
A review of basic to clinical studies of the association between hyperammonemia, methamphetamine.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Aug;395(8):921-931. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02248-w. Epub 2022 May 23. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35604430 Review.
-
Neural circuitry and immunity.Immunol Res. 2015 Dec;63(1-3):38-57. doi: 10.1007/s12026-015-8718-1. Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26512000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Finasteride Has Regionally Different Effects on Brain Oxidative Stress and Acetylcholinesterase Activity in Acute Thioacetamide-Induced Hepatic Encephalopathy in Rats.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 4;10(8):e0134434. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134434. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26241899 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Functional Neuroscience in Immunity.Annu Rev Immunol. 2018 Apr 26;36:783-812. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-042617-053158. Annu Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29677475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive assessment of patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy in Brazil.Metab Brain Dis. 2013 Sep;28(3):473-83. doi: 10.1007/s11011-013-9405-3. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Metab Brain Dis. 2013. PMID: 23625323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar MA, Minarro J, Felipo V. Chronic moderate hyperammonemia impairs active and passive avoidance behaviour and conditional discrimination learning in rats. Exp Neurol. 2000;161:704–13. - PubMed
-
- Amenta F, Tayebati SK, Vitali D, Di Tullio MA. Association with the cholinergic precursor choline alphoscerate and the cholinesterase inhibitor rivastigmine: an approach for enhancing cholinergic neurotransmission. Mech Ageing Dev. 2006;127:173–9. - PubMed
-
- Azorín I, Miñana MD, Felipo V, Grisolía S. A simple animal model of hyperammonemia. Hepatology. 1989;10:311–4. - PubMed
-
- Bartus RT, Dean RL, 3rd, Beer B, Lippa AS. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science. 1982;217:408–14. - PubMed
-
- Beeri R, Andres C, Lev-Lehman E, Timberg R, Huberman T, Shani M, et al. Transgenic expression of human acetylcholinesterase induces progressive cognitive deterioration in mice. Curr Biol. 1995;5:1063–71. - PubMed

