Non-classical genomic estrogen receptor (ER)/specificity protein and ER/activating protein-1 signaling pathways
- PMID: 18772268
- PMCID: PMC2582054
- DOI: 10.1677/JME-08-0103
Non-classical genomic estrogen receptor (ER)/specificity protein and ER/activating protein-1 signaling pathways
Erratum in
- J Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Apr;42(4):359. Kim, Kyoungkim [corrected to Kim, Kyounghyun]
Abstract
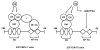
17beta-estradiol binds to the estrogen receptor (ER) to activate gene expression or repression and this involves both genomic (nuclear) and non-genomic (extranuclear) pathways. Genomic pathways include the classical interactions of ligand-bound ER dimers with estrogen-responsive elements in target gene promoters. ER-dependent activation of gene expression also involves DNA-bound ER that subsequently interacts with other DNA-bound transcriptions factors and direct ER-transcription factor (protein-protein) interactions where ER does not bind promoter DNA. Ligand-induced activation of ER/specificity protein (Sp) and ER/activating protein-1 [(AP-1); consisting of jun/fos] complexes are important pathways for modulating expression of a large number of genes. This review summarizes some of the characteristics of ER/Sp- and ER/AP-1-mediated transactivation, which are dependent on ligand structure, cell context, ER-subtype (ERalpha and ERbeta), and Sp protein (SP1, SP3, and SP4) and demonstrates that this non-classical genomic pathway is also functional in vivo.
Figures

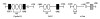
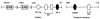


References
-
- Ammendola R, Mesuraca M, Russo T, Cimino F. Sp1 DNA binding efficiency is highly reduced in nuclear extracts from aged rat tissues. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1992;267:17944–17948. - PubMed
-
- Augereau P, Miralles F, Cavailles V, Gaudelet C, Parker M, Rochefort H. Characterization of the proximal estrogen-responsive element of human cathepsin D gene. Molecular Endocrinology. 1994;8:693–703. - PubMed
-
- Bardin A, Moll F, Margueron R, Delfour C, Chu ML, Maudelonde T, Cavailles V, Pujol P. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of fibulin-1 by estrogens leads to differential induction of messenger ribonucleic acid variants in ovarian and breast cancer cells. Endocrinology. 2005;146:760–768. - PubMed
-
- Barkhem T, Haldosen LA, Gustafsson JA, Nilsson S. pS2 Gene expression in HepG2 cells: complex regulation through crosstalk between the estrogen receptor α, an estrogen-responsive element, and the activator protein 1 response element. Molecular Pharmacology. 2002;61:1273–1283. - PubMed
-
- de Medeiros SR Batistuzzo, Krey G, Hihi AK, Wahli W. Functional interactions between the estrogen receptor and the transcription activator Sp1 regulate the estrogen-dependent transcriptional activity of the vitellogenin A1 io promoter. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997;272:18250–18260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

