Candida albicans cell wall proteins
- PMID: 18772287
- PMCID: PMC2546859
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00032-07
Candida albicans cell wall proteins
Abstract
The Candida albicans cell wall maintains the structural integrity of the organism in addition to providing a physical contact interface with the environment. The major components of the cell wall are fibrillar polysaccharides and proteins. The proteins of the cell wall are the focus of this review. Three classes of proteins are present in the candidal cell wall. One group of proteins attach to the cell wall via a glycophosphatidylinositol remnant or by an alkali-labile linkage. A second group of proteins with N-terminal signal sequences but no covalent attachment sequences are secreted by the classical secretory pathway. These proteins may end up in the cell wall or in the extracellular space. The third group of proteins lack a secretory signal, and the pathway(s) by which they become associated with the surface is unknown. Potential constituents of the first two classes have been predicted from analysis of genome sequences. Experimental analyses have identified members of all three classes. Some members of each class selected for consideration of confirmed or proposed function, phenotypic analysis of a mutant, and regulation by growth conditions and transcription factors are discussed in more detail.
Figures
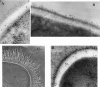
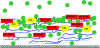
References
-
- Alberti-Segui, C., A. J. Morales, H. Xing, M. M. Kessler, D. A. Willins, K. G. Weinstock, G. Cottarel, K. Fechtel, and B. Rogers. 2004. Identification of potential cell-surface proteins in Candida albicans and investigation of the role of a putative cell-surface glycosidase in adhesion and virulence. Yeast 21285-302. - PubMed
-
- Alberts, B., A. Johnson, J. Lewis, M. Raff, K. Roberts, and P. Walter. 2008. Molecular biology of the cell, 5th ed. Garland Science, Taylor & Francis Group, New York, NY.
-
- Albrecht, A., A. Felk, I. Pichova, J. R. Naglik, M. Schaller, P. de Groot, D. Maccallum, F. C. Odds, W. Schafer, F. Klis, M. Monod, and B. Hube. 2006. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteases of Candida albicans target proteins necessary for both cellular processes and host-pathogen interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 281688-694. - PubMed
-
- Alloush, H. M., J. L. Lopez-Ribot, and W. L. Chaffin. 1996. Dynamic expression of cell wall proteins of Candida albicans revealed by probes from cDNA clones. J. Med. Vet. Mycol. 3491-97. - PubMed
-
- Alloush, H. M., J. L. Lopez-Ribot, B. J. Masten, and W. L. Chaffin. 1997. 3-Phosphoglycerate kinase: a glycolytic enzyme protein present in the cell wall of Candida albicans. Microbiology 143321-330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

