Apoptosis-induced compensatory proliferation. The Cell is dead. Long live the Cell!
- PMID: 18774295
- PMCID: PMC2705980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.08.001
Apoptosis-induced compensatory proliferation. The Cell is dead. Long live the Cell!
Abstract
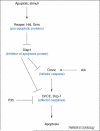
In multi-cellular organisms, activation of apoptosis can trigger compensatory proliferation in surrounding cells to maintain tissue homeostasis. Genetic studies in Drosophila have indicated that distinct mechanisms of compensatory proliferation are employed in apoptotic tissues of different developmental states. In proliferating eye and wing tissues, the initiator caspase Dronc coordinates cell death and compensatory proliferation through the Jun N-terminal kinase and p53. The mitogens Decapentaplegic and Wingless are induced in this process. By contrast, in differentiating eye tissues, the effector caspases DrICE and Dcp-1 activate the Hedgehog signaling pathway to induce compensatory proliferation. In this review, we summarize these findings and discuss how activation of apoptosis is linked to the process of compensatory proliferation. The developmental and pathological relevance of compensatory proliferation is also discussed.
Figures



References
-
- Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ. Cell death: critical control points. Cell. 2004;116:205–219. - PubMed
-
- Haynie JL, Bryant PJ. The effects of X-rays on the proliferation dynamics of cells in the imaginal disc of Drosophila melanagaster. Rouxs Arch. Dev. Biol. 1977;183:85–100. - PubMed
-
- James AA, Bryant PJ. A quantitative study of cell death and mitotic inhibition in γ-irradiated imaginal wing discs of Drosophila melanogaster. Radiat. Res. 1981;87:552–564. - PubMed
-
- Valentin-Vega YA, et al. The intestinal epithelium compensates for p53-mediated cell death and guarantees organismal survival. Cell Death Differ. 2008. DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2008.109 (http://www.nature.com/cdd) - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

