TLR3 and TLR4 expression in healthy and diseased human endometrium
- PMID: 18775079
- PMCID: PMC2543020
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-6-40
TLR3 and TLR4 expression in healthy and diseased human endometrium
Abstract
Background: Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play an essential role in the innate immune system by initiating and directing immune response to pathogens. TLRs are expressed in the human endometrium and their regulation might be crucial for the pathogenesis of endometrial diseases.
Methods: TLR3 and TLR4 expression was investigated during the menstrual cycle and in postmenopausal endometrium considering peritoneal endometriosis, hyperplasia, and endometrial adenocarcinoma specimens (grade 1 to 3). The expression studies applied quantitative RT-PCR and immunolabelling of both proteins.
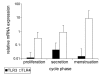
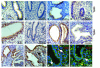
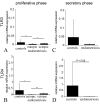
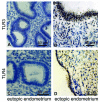
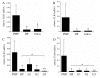
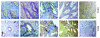
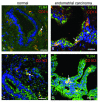
Results: TLR3 and TLR4 proteins were mostly localised to the glandular and luminal epithelium. In addition, TLR4 was present on endometrial dendritic cells, monocytes and macrophages. TLR3 and TLR4 mRNA levels did not show significant changes during the menstrual cycle. In patients with peritoneal endometriosis, TLR3 and TLR4 mRNA expression decreased significantly in proliferative diseased endometrium compared to controls. Interestingly, ectopic endometriotic lesions showed a significant increase of TLR3 und TLR4 mRNA expression compared to corresponding eutopic tissues, indicating a local gain of TLR expression. Endometrial hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma revealed significantly reduced receptor levels when compared with postmenopausal controls. The lowest TLR expression levels were determined in poor differentiated carcinoma (grade 3).
Conclusion: Our data suggest an involvement of TLR3 and TLR4 in endometrial diseases as demonstrated by altered expression levels in endometriosis and endometrial cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impaired CRH and urocortin expression and function in eutopic endometrium of women with endometriosis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Apr;96(4):1145-50. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-2263. Epub 2011 Feb 2. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21289256
-
Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis and Endometrial Adenocarcinoma Express High Levels of Myostatin and Its Receptors Messenger RNAs.Reprod Sci. 2017 Dec;24(12):1577-1582. doi: 10.1177/1933719117698579. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Reprod Sci. 2017. PMID: 28345488
-
Relationship between Toll-like receptor-4 and mPGES-1 gene expression in local lesions of endometriosis patients.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2013 Mar;69(3):231-9. doi: 10.1111/aji.12056. Epub 2012 Dec 17. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23252918
-
Progesterone Resistance in Endometriosis: an Acquired Property?Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Aug;29(8):535-548. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2018.05.006. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 29934050 Review.
-
Modeling Endometrium Biology and Disease.J Pers Med. 2022 Jun 27;12(7):1048. doi: 10.3390/jpm12071048. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35887546 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endometriosis Associated Infertility: A Critical Review and Analysis on Etiopathogenesis and Therapeutic Approaches.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Sep 9;56(9):460. doi: 10.3390/medicina56090460. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32916976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of toll-like receptors (TLRs) and their therapeutic applications in endometrial cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Apr;25(4):859-865. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-02999-1. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36374404 Review.
-
Toll-like receptor (TLR) and nucleosome-binding oligomerization domain (NOD) gene polymorphisms and endometrial cancer risk.BMC Cancer. 2010 Jul 21;10:382. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-382. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20646321 Free PMC article.
-
Endometriosis: An Immunologist's Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 28;26(11):5193. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115193. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-Like Receptor 2 Expression as a New Hallmark of Advanced Endometriosis.Cells. 2020 Jul 30;9(8):1813. doi: 10.3390/cells9081813. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32751735 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:335–376. - PubMed
-
- Cario E, Rosenberg IM, Brandwein SL, Beck PL, Reinecker HC, Podolsky DK. Lipopolysaccharide activates distinct signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cell lines expressing Toll-like receptors. J Immunol. 2000;164:966–972. - PubMed
-
- Fazeli A, Bruce C, Anumba DO. Characterization of Toll-like receptors in the female reproductive tract in humans. Hum Reprod. 2005;20:1372–1378. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

