In vivo imaging of oskar mRNA transport reveals the mechanism of posterior localization
- PMID: 18775316
- PMCID: PMC2585615
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.06.053
In vivo imaging of oskar mRNA transport reveals the mechanism of posterior localization
Abstract
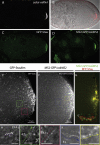
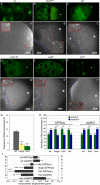
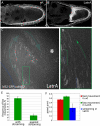
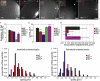
oskar mRNA localization to the posterior of the Drosophila oocyte defines where the abdomen and germ cells form in the embryo. Although this localization requires microtubules and the plus end-directed motor, kinesin, its mechanism is controversial and has been proposed to involve active transport to the posterior, diffusion and trapping, or exclusion from the anterior and lateral cortex. By following oskar mRNA particles in living oocytes, we show that the mRNA is actively transported along microtubules in all directions, with a slight bias toward the posterior. This bias is sufficient to localize the mRNA and is reversed in mago, barentsz, and Tropomyosin II mutants, which mislocalize the mRNA anteriorly. Since almost all transport is mediated by kinesin, oskar mRNA localizes by a biased random walk along a weakly polarized cytoskeleton. We also show that each component of the oskar mRNA complex plays a distinct role in particle formation and transport.
Figures

Comment in
-
Highways for mRNA transport.Cell. 2008 Sep 5;134(5):722-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.020. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18775304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bashirullah A., Cooperstock R., Lipshitz H. RNA localization in development. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998;67:335–394. - PubMed
-
- Beach D., Salmon E., Bloom K. Localization and anchoring of mRNA in budding yeast. Curr. Biol. 1999;9:569–578. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand E., Chartrand P., Schaefer M., Shenoy S., Singer R., Long R. Localization of ASH1 mRNA particles in living yeast. Mol. Cell. 1998;2:437–445. - PubMed
-
- Boswell R.E., Prout M.E., Steichen J.C. Mutations in a newly identified Drosophila melanogaster gene, mago nashi, disrupt germ cell formation and result in the formation of mirror-image symmetrical double abdomen embryos. Development. 1991;113:373–384. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

