The multiple roles of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in mast cell biology
- PMID: 18775670
- PMCID: PMC2706663
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2008.07.004
The multiple roles of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in mast cell biology
Abstract
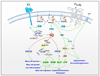
Mast cells play a central role in the initiation of inflammatory responses associated with asthma and other allergic disorders. Receptor-mediated mast cell growth, differentiation, homing to their target tissues, survival and activation are all controlled, to varying degrees, by phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)-driven pathways. It is not fully understood how such diverse responses can be differentially regulated by PI3K. However, recent studies have provided greater insight into the mechanisms that control, and those that are controlled by, different PI3K subunit isoforms in mast cells. In this review, we discuss how PI3K influences the mast cell processes described above. Furthermore, we describe how different mast cell receptors use alternative isoforms of PI3K for these functions and discuss potential downstream targets of these isoforms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mekori YA, Metcalfe DD. Mast cells in innate immunity. Immunol Rev. 2000;173:131–140. - PubMed
-
- Galli SJ, et al. Mast cells in the development of adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:135–142. - PubMed
-
- Metcalfe DD, et al. Mast cells. Physiol Rev. 1997;77:1033–1079. - PubMed
-
- Gould HJ, Sutton BJ. IgE in allergy and asthma today. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:205–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

