Transcriptome analyses show changes in gene expression to accompany pollen germination and tube growth in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 18775970
- PMCID: PMC2577266
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.108.126375
Transcriptome analyses show changes in gene expression to accompany pollen germination and tube growth in Arabidopsis
Abstract
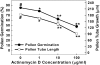
Pollen germination, along with pollen tube growth, is an essential process for the reproduction of flowering plants. The germinating pollen with tip-growth characteristics provides an ideal model system for the study of cell growth and morphogenesis. As an essential step toward a detailed understanding of this important process, the objective of this study was to comprehensively analyze the transcriptome changes during pollen germination and pollen tube growth. Using Affymetrix Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) ATH1 Genome Arrays, this study is, to our knowledge, the first to show the changes in the transcriptome from desiccated mature pollen grains to hydrated pollen grains and then to pollen tubes of Arabidopsis. The number of expressed genes, either for total expressed genes or for specifically expressed genes, increased significantly from desiccated mature pollen to hydrated pollen and again to growing pollen tubes, which is consistent with the finding that pollen germination and tube growth were significantly inhibited in vitro by a transcriptional inhibitor. The results of Gene Ontology analyses showed that expression of genes related to cell rescue, transcription, signal transduction, and cellular transport was significantly changed, especially for up-regulation, during pollen germination and tube growth. In particular, genes of the calmodulin/calmodulin-like protein, cation/hydrogen exchanger, and heat shock protein families showed the most significant changes during pollen germination and tube growth. These results demonstrate that the overall transcription of genes, both in the number of expressed genes and in the levels of transcription, was increased. Furthermore, the appearance of many novel transcripts during pollen germination as well as tube growth indicates that these newly expressed genes may function in this complex process.
Figures

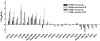
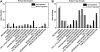
Comment in
-
Ion transporters involved in pollen germination and pollen tube tip-growth.Plant Signal Behav. 2009 Dec;4(12):1193-5. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.12.10063. Plant Signal Behav. 2009. PMID: 20514245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boavida LC, McCormick S (2007) Temperature as a determinant factor for increased and reproducible in vitro pollen germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 52 570–582 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

