Physiological properties of hERG 1a/1b heteromeric currents and a hERG 1b-specific mutation associated with Long-QT syndrome
- PMID: 18776039
- PMCID: PMC2761010
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.185249
Physiological properties of hERG 1a/1b heteromeric currents and a hERG 1b-specific mutation associated with Long-QT syndrome
Abstract
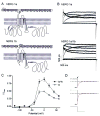
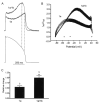
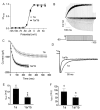
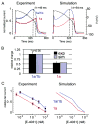
Cardiac I Kr is a critical repolarizing current in the heart and a target for inherited and acquired long-QT syndrome (LQTS). Biochemical and functional studies have demonstrated that I Kr channels are heteromers composed of both hERG 1a and 1b subunits, yet our current understanding of I Kr functional properties derives primarily from studies of homooligomers of the original hERG 1a isolate. Here, we examine currents produced by hERG 1a and 1a/1b channels expressed in HEK-293 cells at near-physiological temperatures. We find that heteromeric hERG 1a/1b currents are much larger than hERG 1a currents and conduct 80% more charge during an action potential. This surprising difference corresponds to a 2-fold increase in the apparent rates of activation and recovery from inactivation, thus reducing rectification and facilitating current rebound during repolarization. Kinetic modeling shows these gating differences account quantitatively for the differences in current amplitude between the 2 channel types. Drug sensitivity was also different. Compared to homomeric 1a channels, heteromeric 1a/1b channels were inhibited by E-4031 with a slower time course and a corresponding 4-fold shift in the IC50. The importance of hERG 1b in vivo is supported by the identification of a 1b-specific A8V missense mutation in 1/269 unrelated genotype-negative LQTS patients that was absent in 400 control alleles. Mutant 1bA8V expressed alone or with hERG 1a in HEK-293 cells dramatically reduced 1b protein levels. Thus, mutations specifically disrupting hERG 1b function are expected to reduce cardiac I Kr and enhance drug sensitivity, and represent a potential mechanism underlying inherited or acquired LQTS.
Figures







Similar articles
-
hERG 1a LQT2 C-terminus truncation mutants display hERG 1b-dependent dominant negative mechanisms.Heart Rhythm. 2016 May;13(5):1121-1130. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2016.01.012. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Heart Rhythm. 2016. PMID: 26775140
-
hERG subunit composition determines differential drug sensitivity.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;164(2b):419-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01378.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21449979 Free PMC article.
-
[HERG K+ channel, the target of anti-arrhythmias drugs].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007 Jul;42(7):687-91. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17882949 Review. Chinese.
-
hERG 1b is critical for human cardiac repolarization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Dec 16;111(50):18073-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1414945111. Epub 2014 Dec 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25453103 Free PMC article.
-
The cardiac hERG/IKr potassium channel as pharmacological target: structure, function, regulation, and clinical applications.Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(18):2271-83. doi: 10.2174/138161206777585102. Curr Pharm Des. 2006. PMID: 16787254 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional expression of potassium channels in cardiomyocytes derived from embryonic stem cells.Res Pharm Sci. 2012 Jan;7(1):1-11. Res Pharm Sci. 2012. PMID: 23181074 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of hERG1 channel isoforms reproduces properties of native I(Kr) and modulates cardiac action potential characteristics.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 2;5(2):e9021. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009021. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20126398 Free PMC article.
-
A PAS-targeting hERG1 activator reduces arrhythmic events in Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome patient-derived hiPSC-CMs.JCI Insight. 2025 Jan 9;10(4):e183444. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.183444. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 39786967 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the hERG potassium channel by phenanthrene: a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutant.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(23):7899-7914. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03967-8. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34727194 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological characterization of the modified hERGT potassium channel used to obtain the first cryo-EM hERG structure.Physiol Rep. 2020 Oct;8(20):e14568. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14568. Physiol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33091232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanguinetti MC, Jurkiewicz NK. Delayed rectifier outward K+ current is composed of two currents in guinea pig atrial cells. Am J Physiol. 1991;260:H393–399. - PubMed
-
- Sanguinetti MC, Jiang C, Curran ME, Keating MT. A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell. 1995;81:299–307. - PubMed
-
- Trudeau MC, Warmke JW, Ganetzky B, Robertson GA. HERG, a human inward rectifier in the voltage-gated potassium channel family. Science. 1995;269:92–95. - PubMed
-
- Curran ME, Splawski I, Timothy KW, Vincent GM, Green ED, Keating MT. A molecular basis for cardiac arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell. 1995;80:795–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

