Systematic assessment of copy number variant detection via genome-wide SNP genotyping
- PMID: 18776910
- PMCID: PMC2759751
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.236
Systematic assessment of copy number variant detection via genome-wide SNP genotyping
Abstract
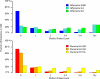
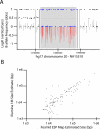
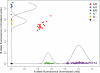
SNP genotyping has emerged as a technology to incorporate copy number variants (CNVs) into genetic analyses of human traits. However, the extent to which SNP platforms accurately capture CNVs remains unclear. Using independent, sequence-based CNV maps, we find that commonly used SNP platforms have limited or no probe coverage for a large fraction of CNVs. Despite this, in 9 samples we inferred 368 CNVs using Illumina SNP genotyping data and experimentally validated over two-thirds of these. We also developed a method (SNP-Conditional Mixture Modeling, SCIMM) to robustly genotype deletions using as few as two SNP probes. We find that HapMap SNPs are strongly correlated with 82% of common deletions, but the newest SNP platforms effectively tag about 50%. We conclude that currently available genome-wide SNP assays can capture CNVs accurately, but improvements in array designs, particularly in duplicated sequences, are necessary to facilitate more comprehensive analyses of genomic variation.
Figures

References
-
- Sebat J, et al. Large-scale copy number polymorphism in the human genome. Science. 2004;305:525–8. - PubMed
-
- Tuzun E, et al. Fine-scale structural variation of the human genome. Nat Genet. 2005;37:727–32. - PubMed
-
- Cooper GM, Nickerson DA, Eichler EE. Mutational and selective effects on copy-number variants in the human genome. Nat Genet. 2007;39:S22–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

