Comparative analysis of mRNA targets for human PUF-family proteins suggests extensive interaction with the miRNA regulatory system
- PMID: 18776931
- PMCID: PMC2522278
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003164
Comparative analysis of mRNA targets for human PUF-family proteins suggests extensive interaction with the miRNA regulatory system
Abstract
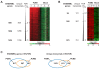
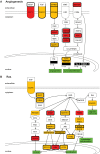
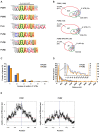
Genome-wide identification of mRNAs regulated by RNA-binding proteins is crucial to uncover post-transcriptional gene regulatory systems. The conserved PUF family RNA-binding proteins repress gene expression post-transcriptionally by binding to sequence elements in 3'-UTRs of mRNAs. Despite their well-studied implications for development and neurogenesis in metazoa, the mammalian PUF family members are only poorly characterized and mRNA targets are largely unknown. We have systematically identified the mRNAs associated with the two human PUF proteins, PUM1 and PUM2, by the recovery of endogenously formed ribonucleoprotein complexes and the analysis of associated RNAs with DNA microarrays. A largely overlapping set comprised of hundreds of mRNAs were reproducibly associated with the paralogous PUM proteins, many of them encoding functionally related proteins. A characteristic PUF-binding motif was highly enriched among PUM bound messages and validated with RNA pull-down experiments. Moreover, PUF motifs as well as surrounding sequences exhibit higher conservation in PUM bound messages as opposed to transcripts that were not found to be associated, suggesting that PUM function may be modulated by other factors that bind conserved elements. Strikingly, we found that PUF motifs are enriched around predicted miRNA binding sites and that high-confidence miRNA binding sites are significantly enriched in the 3'-UTRs of experimentally determined PUM1 and PUM2 targets, strongly suggesting an interaction of human PUM proteins with the miRNA regulatory system. Our work suggests extensive connections between the RBP and miRNA post-transcriptional regulatory systems and provides a framework for deciphering the molecular mechanism by which PUF proteins regulate their target mRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Moore MJ. From birth to death: the complex lives of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science. 2005;309:1514–1518. - PubMed
-
- Dreyfuss G, Kim VN, Kataoka N. Messenger-RNA-binding proteins and the messages they carry. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:195–205. - PubMed
-
- St Johnston D. Moving messages: the intracellular localization of mRNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:363–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

