Genome-wide association of histone H3 lysine nine methylation with CHG DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 18776934
- PMCID: PMC2522283
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003156
Genome-wide association of histone H3 lysine nine methylation with CHG DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
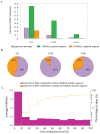
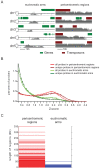
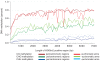
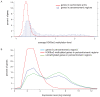
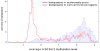
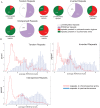
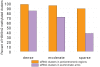
Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9) is a hallmark of transcriptional silencing in many organisms. In Arabidopsis thaliana, dimethylation of H3K9 (H3K9m2) is important in the silencing of transposons and in the control of DNA methylation. We constructed a high-resolution genome-wide map of H3K9m2 methylation by using chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with whole genome Roche Nimblegen microarrays (ChIP-chip). We observed a very high coincidence between H3K9m2 and CHG methylation (where H is either A,T or C) throughout the genome. The coding regions of genes that are associated exclusively with methylation in a CG context did not contain H3K9m2. In addition, we observed two distinct patterns of H3K9m2. Transposons and other repeat elements present in the euchromatic arms contained small islands of H3K9m2 present at relatively low levels. In contrast, pericentromeric/centromeric regions of Arabidopsis chromosomes contained long, rarely interrupted blocks of H3K9m2 present at much higher average levels than seen in the chromosome arms. These results suggest a complex interplay between H3K9m2 and different types of DNA methylation and suggest that distinct mechanisms control H3K9m2 in different compartments of the genome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128:693–705. - PubMed
-
- Peters AH, O'Carroll D, Scherthan H, Mechtler K, Sauer S, et al. Loss of the suv39h histone methyltransferases impairs mammalian heterochromatin and genome stability. Cell. 2001;107:323–337. - PubMed
-
- Lehnertz B, Ueda Y, Derijck AA, Braunschweig U, Perez-Burgos L, et al. Suv39h-mediated histone H3 lysine 9 methylation directs DNA methylation to major satellite repeats at pericentric heterochromatin. Curr Biol. 2003;13:1192–1200. - PubMed
-
- Tachibana M, Sugimoto K, Fukushima T, Shinkai Y. Set domain-containing protein, G9a, is a novel lysine-preferring mammalian histone methyltransferase with hyperactivity and specific selectivity to lysines 9 and 27 of histone H3. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:25309–25317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

