Myocardial tissue Doppler echocardiography and N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in diastolic and systolic heart failure
- PMID: 18778476
- PMCID: PMC2542999
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7120-6-45
Myocardial tissue Doppler echocardiography and N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in diastolic and systolic heart failure
Abstract
Background: The aim of this prospective study was to assess the diagnostic value of NT-proBNP and the concordance with Tissue Doppler Echocardiography (including strain and longitudinal displacement) in diastolic and systolic heart failure.
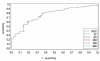
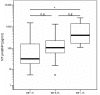
Methods and results: 137 consecutive clinically stable patients were included (42 healthy controls, 43 with diastolic heart failure, 52 with systolic heart failure). In diastolic heart failure, basal septal strain was reduced (-24.8 +/- 8.1% vs. controls. -18.5 +/- 5.3%, p < 0.0001). In all patients with preserved systolic function, septal basal longitudinal displacement was impaired in patients with increased left-ventricular filling pressures (E/E' < 8: 13.5 mm +/- 3.3 mm vs. E/E' > 15: 8.5 mm +/- 2.3 mm, p = 0.001) parallel to NT-proBNP elevation (E/E' < 8: 45.8 pg/ml, IQR: 172.5 pg/ml vs. E/E' > 15: 402.0 pg/ml, IQR: 1337.2 pg/ml; p = 0.0007). In ROC analysis, NT-proBNP could detect patients with reduced left ventricular systolic function (LVEF >or= 55%) with a good diagnostic accuracy. However, the diagnostic accuracy of NT-proBNP to detect diastolic dysfunction was lower.
Conclusion: Subtle changes of longitudinal myocardial function begin in diastolic heart failure and are further increased in systolic heart failure. In patients with preserved LV function, a complex approach with the integration of multiple parameters including Tissue Doppler echocardiography and NT-proBNP is necessary to classify patients.
Figures


References
-
- Yancy CW, Lopatin M, Stevenson LW, De Marco T, Fonarow GC, ADHERE Scientific Advisory Committee and Investigators Clinical presentation, management, and in-hospital outcomes of patients admitted with acute decompensated heart failure with preserved systolic function: a report from the Acute Decompensated Heart Failure National Registry (ADHERE) Database. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:76–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.09.022. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

