Action in the axon: generation and transport of signaling endosomes
- PMID: 18778772
- PMCID: PMC2693191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.08.005
Action in the axon: generation and transport of signaling endosomes
Abstract
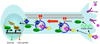
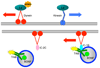
Neurons extend axonal processes over long distances, necessitating efficient transport mechanisms to convey target-derived neurotrophic survival signals from remote distal axons to cell bodies. Retrograde transport, powered by dynein motors, supplies cell bodies with survival signals in the form of 'signaling endosomes'. In this review, we will discuss new advances in our understanding of the motor proteins that bind to and move signaling components in a retrograde direction and discuss mechanisms that might specify distinct neuronal responses to spatially restricted neurotrophin signals. Disruption of retrograde transport leads to a variety of neurodegenerative diseases, highlighting the role of retrograde transport of signaling endosomes for axonal maintenance and the importance of efficient transport for neuronal survival and function.
Figures
References
-
- Miller FD, Kaplan DR. On Trk for retrograde signaling. Neuron. 2001;32:767–770. - PubMed
-
- Segal RA. Selectivity in neurotrophin signaling: theme and variations. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003;26:299–330. - PubMed
-
- Ginty DD, Segal RA. Retrograde neurotrophin signaling: Trk-ing along the axon. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2002;12:268–274. - PubMed
-
- Heerssen HM, Pazyra MF, Segal RA. Dynein motors transport activated Trks to promote survival of target-dependent neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7:596–604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

