Receptor trafficking controls weak signal delivery: a strategy used by c-Met for STAT3 nuclear accumulation
- PMID: 18779368
- PMCID: PMC2528569
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200806076
Receptor trafficking controls weak signal delivery: a strategy used by c-Met for STAT3 nuclear accumulation
Abstract
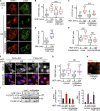
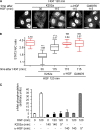
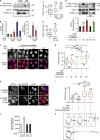
C-Met, the receptor of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), through overexpression or mutation, is a major protooncogene that provides an attractive molecular target for cancer therapy. HGF/c-Met-induced tumorigenesis is dependent, in part, on the transcription factor and oncogene signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), which is believed to be activated by the receptor at the plasma membrane and then to travel to the nucleus where it acts. We demonstrate that although the robust signal to STAT3 elicited from the cytokine oncostatin-M does indeed support this mechanism of STAT3 action, for the weaker STAT3 signal emanating from c-Met, the activated receptor itself needs to be delivered to a perinuclear endosomal compartment to sustain phosphorylated STAT3 in the nucleus. This is signal specific because c-Met-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase nuclear accumulation does not require receptor trafficking to the perinuclear compartment. This response is triggered from peripheral endosomes. Thus, control of growth factor receptor traffic determines the nature of the signal output, providing novel opportunities for intervention.
Figures


Comment in
-
Survival of the weakest: signaling aided by endosomes.J Cell Biol. 2008 Sep 8;182(5):823-5. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200807165. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18779366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birchmeier, C., W. Birchmeier, E. Gherardi, and G.F. Vande Woude. 2003. Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:915–925. - PubMed
-
- Boccaccio, C., M. Ando, L. Tamagnone, A. Bardelli, P. Michieli, C. Battistini, and P.M. Comoglio. 1998. Induction of epithelial tubules by growth factor HGF depends on the STAT pathway. Nature. 391:285–288. - PubMed
-
- Christensen, J.G., J. Burrows, and R. Salgia. 2005. c-Met as a target for human cancer and characterization of inhibitors for therapeutic intervention. Cancer Lett. 225:1–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

