IL-21 signaling is critical for the development of type I diabetes in the NOD mouse
- PMID: 18779574
- PMCID: PMC2544573
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0804358105
IL-21 signaling is critical for the development of type I diabetes in the NOD mouse
Abstract
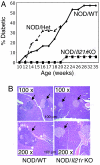
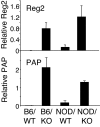
IL-21 is a pleiotropic type I cytokine that shares the common cytokine receptor gamma chain and plays important roles for normal Ig production, terminal B cell differentiation to plasma cells, and Th17 differentiation. IL-21 is elevated in several autoimmune diseases, and blocking its action has attenuated disease in MRL/lpr mice and in collagen-induced arthritis. The diabetes-associated Idd3 locus is at the Il2/Il21 locus, and elevated IL-21 was observed in the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse and suggested to contribute to diabetes by augmenting T cell homeostatic proliferation. To determine the role of IL-21 in diabetes, Il21r-knockout (KO) mice were backcrossed to NOD mice. These mice were devoid of lymphocytic infiltration into the pancreas, and only 1 of 20 animals had an elevated glucose compared with 60% of NOD mice on a wild-type (WT) background. Although TCR and Treg-related responses were normal, these mice had reduced Th17 cells and significantly higher levels of mRNAs encoding members of the Reg (regenerating) gene family whose transgenic expression protects against diabetes. Our studies establish a critical role for IL-21 in the development of type I diabetes in the NOD mouse, with obvious potential implications for type I diabetes in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: R.S. and W.J.L. are inventors on patents and patent applications related to IL-21.
Figures



References
-
- Powers AC. Diabetes Mellitus. New York: McGraw–Hill; 2005.
-
- Anderson M, Bluestone J. The NOD mouse: A model of immune dysregulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:447–485. - PubMed
-
- Parrish-Novak J, et al. Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature. 2000;408:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Spolski R, Leonard WJ. Interleukin-21: Basic biology and implications for cancer and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:57–79. - PubMed
-
- Noguchi M, et al. Interleukin-2 receptor γ chain mutation results in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency in humans. Cell. 1993;73:147–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

