Gene transfer using liposome-complexed adenovirus seems to overcome limitations due to coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor-deficiency of cancer cells, both in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 18779655
- PMCID: PMC2679272
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2008.40.4.427
Gene transfer using liposome-complexed adenovirus seems to overcome limitations due to coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor-deficiency of cancer cells, both in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
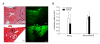
Use of adenoviruses as vehicle for gene therapy requires that target cells express appropriate receptors such as coxsakievirus and adenovirus receptor (CAR). We show here that CAR-deficiency in cancer cells, that limits adenoviral gene delivery, can be overcome by using adenovirus complexed with the liposome, Ad-PEGPE [1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[methoxy(poly-ethylene glycol)-2000]. We first confirmed that CT-26 mouse colon cancer cells are deficient in CAR by RT-PCR, and then showed that CT-26 cells infected with Ad-GFP/PEGPE exhibited highly enhanced expression of green fluorescent protein (GFP), compared with those infected with Ad-GFP. GFP expression depends on the dose of liposome and adenovirus. Luciferase expression in livers treated with Ad-luc/PEGPE was about 1,000-fold less than those infected with Ad-luc. In a liver metastasis mouse tumor model developed by intrasplenic injection of CT-26 cells, luciferase expression following i.v. injection of Ad-luc/PEGPE was significantly higher in tumors than in adjacent non-neoplastic liver. Following systemic administration of Ad-GFP/PEGPE, GFP expression increased in tumors more than in adjacent liver while the reverse was true following administration of Ad-GFP. In the latter case, GFP expression was higher in liver than in tumors. This study demonstrates that systemic delivery of PEGPE-adenovirus complex is an effective tool of adenoviral delivery as it overcomes limitation due to CAR deficiency of target cells while reducing hepatic uptake and enhancing adenoviral gene expression in tumors.
Figures

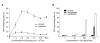

References
-
- Bergelson JM, Cunningham JA, Droguett G, Kurt-Jones EA, Krithivas A, Hong JS, Horwitz MS, Crowell RL, Finberg RW. Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science. 1997;275:1320–1323. - PubMed
-
- Byk T, Haddada H, Vainchenker W, Louache F. Lipofectamine and related cationic lipids strongly improve adenoviral infection efficiency of primitive human hematopoietic cells. Human Gene Ther. 1998;9:2493–2502. - PubMed
-
- Chae HY, Lee BW, Oh SH, Ahn YR, Chung JH, Min YK, Lee MS, Kim KW. Effective glycemic control achieved by transplanting non-viral cationic liposome-mediated VEGF-transfected islets in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Exp Mol Med. 2005;37:513–523. - PubMed
-
- Chillőn M, Lee JH, Fasbender A, Welsh MJ. Adenovirus complexed with polyethylene glycol and cationic lipid is shielded from neutralizing antibodies in vitro. Gene Ther. 1998;5:995–1002. - PubMed
-
- Fasbender A, Zabner J, Chillőn M, Moninger TO, Puga AP, Davidson BL, Welsh MJ. Complexes of adenovirus with polycationic polymers and cationic lipids increase the efficiency of gene transfer in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:6479–6489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
