Rapid molecular detection of rifampicin resistance facilitates early diagnosis and treatment of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis: case control study
- PMID: 18779863
- PMCID: PMC2526158
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003173
Rapid molecular detection of rifampicin resistance facilitates early diagnosis and treatment of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis: case control study
Abstract
Background: Multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a major public health concern since diagnosis is often delayed, increasing the risk of spread to the community and health care workers. Treatment is prolonged, and the total cost of treating a single case is high. Diagnosis has traditionally relied upon clinical suspicion, based on risk factors and culture with sensitivity testing, a process that can take weeks or months. Rapid diagnostic molecular techniques have the potential to shorten the time to commencing appropriate therapy, but have not been put to the test under field conditions.
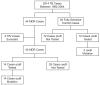
Methodology/principal findings: This retrospective case-control study aimed to identify risk factors for MDR-TB, and analyse the impact of testing for rifampicin resistance using RNA polymerase B (rpoB) mutations as a surrogate for MDR-TB. Forty two MDR-TB cases and 84 fully sensitive TB controls were matched by date of diagnosis; and factors including demographics, clinical presentation, microbiology findings, management and outcome were analysed using their medical records. Conventionally recognised risk factors for MDR-TB were absent in almost half (43%) of the cases, and 15% of cases were asymptomatic. A significant number of MDR-TB cases were identified in new entrants to the country. Using rpoB mutation testing, the time to diagnosis of MDR-TB was dramatically shortened by a median of 6 weeks, allowing patients to be commenced on appropriate therapy a median of 51days earlier than those diagnosed by conventional culture and sensitivity testing.
Conclusions/significance: MDR-TB is frequently an unexpected finding, may be asymptomatic, and is particularly prevalent among TB infected new entrants to the country. Molecular resistance testing of all acid fast bacilli positive specimens has the potential to rapidly identify MDR-TB patients and commence them on appropriate therapy significantly earlier than by conventional methods.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Health Protection Agency, London. Focus on Tuberculosis: Annual surveillance report 2006 - England, Wales and Northern Ireland. 2006. Available: http://www.hpa.org.uk/publications/2006/tb_report/focus_on_tb.pdf. Accessed 2006 Nov.
-
- World Health Organisation. Treatment of Tuberculosis: Guidelines for National Programmes. Third Edition. 2003. Available: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/2003/WHO_CDS_TB_2003.313_eng.pdf. 2003.
-
- Health Protection Agency, London. The UK Mycobacterial Surveillance Network Report, 1994–2003. 10 years of MycobNet. 2005. Available: http://www.hpa.org.uk/infections/topics_az/tb/pdf/MycobNet_10_Year_Repor.... Accessed 2005 Dec.
-
- Aziz M, Wright A, Laszlo A, De Muynck A, Portaels F, Van Deun A, Wells C, Nunn P, Blanc L, Raviglione MC. Epidemiology of antituberculosis drug resistance (the Global Project on Anti-tuberculosis Drug Resistance Surveillance): an updated analysis. Lancet. 2006;368:2142–2154. - PubMed