CXCR4 in Cancer and Its Regulation by PPARgamma
- PMID: 18779872
- PMCID: PMC2528256
- DOI: 10.1155/2008/769413
CXCR4 in Cancer and Its Regulation by PPARgamma
Abstract
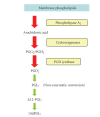
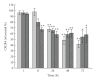
Chemokines are peptide mediators involved in normal development, hematopoietic and immune regulation, wound healing, and inflammation. Among the chemokines is CXCL12, which binds principally to its receptor CXCR4 and regulates leukocyte precursor homing to bone marrow and other sites. This role of CXCL12/CXCR4 is "commandeered" by cancer cells to facilitate the spread of CXCR4-bearing tumor cells to tissues with high CXCL12 concentrations. High CXCR4 expression by cancer cells predisposes to aggressive spread and metastasis and ultimately to poor patient outcomes. As well as being useful as a marker for disease progression, CXCR4 is a potential target for anticancer therapies. It is possible to interfere directly with the CXCL12:CXCR4 axis using peptide or small-molecular-weight antagonists. A further opportunity is offered by promoting strategies that downregulate CXCR4 pathways: CXCR4 expression in the tumor microenvironment is modulated by factors such as hypoxia, nucleosides, and eicosanoids. Another promising approach is through targeting PPAR to suppress CXCR4 expression. Endogenous PPARgamma such as 15-deoxy-Delta(12,14)-PGJ(2) and synthetic agonists such as the thiazolidinediones both cause downregulation of CXCR4 mRNA and receptor. Adjuvant therapy using PPARgamma agonists may, by stimulating PPARgamma-dependent downregulation of CXCR4 on cancer cells, slow the rate of metastasis and impact beneficially on disease progression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
15-Deoxy-delta(12,14)-prostaglandin J(2) down-regulates CXCR4 on carcinoma cells through PPARgamma- and NFkappaB-mediated pathways.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Oct 1;313(16):3446-58. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.06.027. Epub 2007 Jul 13. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17707368
-
Biological/pathological functions of the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axes in the pathogenesis of bladder cancer.Int J Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec;22(6):991-1000. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1187-x. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Int J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29022185 Review.
-
Ligand-activated PPARγ downregulates CXCR4 gene expression through a novel identified PPAR response element and inhibits breast cancer progression.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 4;7(40):65109-65124. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11371. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27556298 Free PMC article.
-
The chemokine receptors CXCR4/CXCR7 and their primary heterodimeric ligands CXCL12 and CXCL12/high mobility group box 1 in pancreatic cancer growth and development: finding flow.Pancreas. 2015 May;44(4):528-34. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000298. Pancreas. 2015. PMID: 25872129 Review.
-
The CXCL12-CXCR4 Signaling Axis Plays a Key Role in Cancer Metastasis and is a Potential Target for Developing Novel Therapeutics against Metastatic Cancer.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(33):5543-5561. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666191113113110. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31724498
Cited by
-
Impact of the hypoxic tumor microenvironment on the regulation of cancer stem cell characteristics.Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Jun 15;9(12):949-56. doi: 10.4161/cbt.9.12.12347. Epub 2010 Jun 11. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20581454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists modulate neuropathic pain: a link to chemokines?Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Aug 20;8:238. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00238. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25191225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 is closely correlated with clinical outcome in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 May;37(5):6099-105. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4464-1. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26611644
-
Dipyrimidine amines: a novel class of chemokine receptor type 4 antagonists with high specificity.J Med Chem. 2010 Dec 23;53(24):8556-68. doi: 10.1021/jm100786g. Epub 2010 Nov 24. J Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 21105715 Free PMC article.
-
Does Oral Apigenin Have Real Potential for a Therapeutic Effect in the Context of Human Gastrointestinal and Other Cancers?Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 18;12:681477. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.681477. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34084146 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balabanian K, Lagane B, Infantino S, et al. The chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12 binds to and signals through the orphan receptor RDC1 in T lymphocytes. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2005;280(42):35760–35766. - PubMed
-
- Murphy PM, Baggiolini M, Charo IF, et al. International union of pharmacology. XXII. Nomenclature for chemokine receptors. Pharmacological Reviews. 2000;52(1):145–176. - PubMed
-
- Mellado M, Rodríguez-Frade JM, Mañes S, Martínez-A C. Chemokine signaling and functional responses: the role of receptor dimerization and TK pathway activation. Annual Review of Immunology. 2001;19:397–421. - PubMed
-
- Rossi D, Zlotnik A. The biology of chemokines and their receptors. Annual Review of Immunology. 2000;18:217–243. - PubMed
-
- Foord SM, Bonner TI, Neubig RR, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVI. G protein-coupled receptor list. Pharmacological Reviews. 2005;57(2):279–288. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

