Deregulation of MUC4 in gastric adenocarcinoma: potential pathobiological implication in poorly differentiated non-signet ring cell type gastric cancer
- PMID: 18781152
- PMCID: PMC2538752
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604632
Deregulation of MUC4 in gastric adenocarcinoma: potential pathobiological implication in poorly differentiated non-signet ring cell type gastric cancer
Abstract
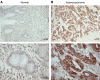
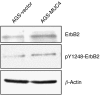
MUC4 is a large, heavily glycosylated transmembrane mucin, that is implicated in the pathogenesis of various types of cancers. To date, no extensive study has been done to check the expression and functional significance of MUC4 in different types of gastric adenocarcinomas. Here, we report the expression profile of MUC4 in gastric adenocarcinomas and its function in poorly differentiated gastric non-signet ring cell carcinoma (non-SRCC) type cells. Immunohistochemical analysis using tissue microarray (TMA) showed a significant difference in MUC4 expression between normal adjacent (n = 45) and gastric adenocarcinoma (n = 83; P < 0.001). MUC4 expression was not associated with tumour type, stage or with the degree of differentiation. To gain further insight into the significance of MUC4 expression in gastric non-SRCC cells, MUC4 was ectopically expressed in AGS, a poorly differentiated gastric non-signet ring cell line. The MUC4 overexpressing cells (AGS-MUC4) showed a significant increase (P < 0.005) in cell motility and a decrease in cellular aggregation as compared with the vector-transfected cells. Furthermore, in vivo tumorigenicity analysis revealed that animals transplanted with the MUC4 overexpressing cells (AGS-MUC4) had a greater incidence of tumours (83%) in comparison to empty vector control (17%). In addition, the expression of MUC4 resulted in enhanced expression of total cellular ErbB2 and phosphorylated ErbB2. In conclusion, our results showed that MUC4 is overexpressed in gastric adenocarcinoma tissues, and that it has a role in promoting aggressive properties in poorly differentiated gastric non-SRCC cells through the activation of the ErbB2 oncoprotein.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Establishment and characterization of novel gastric signet-ring cell and non signet-ring cell poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma cell lines with low and high malignant potential.Gastric Cancer. 2013 Jan;16(1):74-83. doi: 10.1007/s10120-012-0149-2. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Gastric Cancer. 2013. PMID: 22450770
-
Muc4 is required for activation of ErbB2 in signet ring carcinoma cell lines.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Mar 30;355(1):200-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.133. Epub 2007 Feb 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17292332
-
Overexpression of c-erbB-2 protein in gastric cancer. Its correlation with long-term survival of patients.Cancer. 1993 Dec 1;72(11):3179-84. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19931201)72:11<3179::aid-cncr2820721108>3.0.co;2-#. Cancer. 1993. PMID: 7902202
-
Breast metastasis of gastric signet-ring cell carcinoma: a case report and literature review.World J Surg Oncol. 2015 Mar 26;13:120. doi: 10.1186/s12957-015-0538-1. World J Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25890325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastric adenocarcinoma of fundic gland type with signet-ring cell carcinoma component: A case report and review of the literature.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jul 14;24(26):2915-2920. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i26.2915. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30018486 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetically engineered mucin mouse models for inflammation and cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015 Dec;34(4):593-609. doi: 10.1007/s10555-015-9549-1. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015. PMID: 25634251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Mucins (MUC) trafficking in benign and malignant conditions.Oncotarget. 2014 Sep 15;5(17):7272-84. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2370. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25261375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucins as contrast agent targets for fluorescence-guided surgery of pancreatic cancer.Cancer Lett. 2023 May 1;561:216150. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216150. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 36997106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Characterization of RNA Editing Sites in Primary Gastric Adenocarcinoma through RNA-seq Data Analysis.Int J Genomics. 2020 Dec 18;2020:6493963. doi: 10.1155/2020/6493963. eCollection 2020. Int J Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33415135 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of membrane-associated mucins 1 and 4 in gastric adenocarcinoma.Exp Ther Med. 2012 Aug;4(2):311-316. doi: 10.3892/etm.2012.598. Epub 2012 Jun 1. Exp Ther Med. 2012. PMID: 23139719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrianifahanana M, Moniaux N, Schmied BM, Ringel J, Friess H, Hollingsworth MA, Buchler MW, Aubert JP, Batra SK (2001) Mucin (MUC) gene expression in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis: a potential role of MUC4 as a tumor marker of diagnostic significance. Clin Cancer Res 7: 4033–4040 - PubMed
-
- Baldus SE, Zirbes TK, Engel S, Hanisch FG, Monig SP, Lorenzen J, Glossmann J, Fromm S, Thiele J, Pichlmaier H, Dienes HP (1998) Correlation of the immunohistochemical reactivity of mucin peptide cores MUC1 and MUC2 with the histopathological subtype and prognosis of gastric carcinomas. Int J Cancer 79: 133–138 - PubMed
-
- Barranco SC, Townsend Jr CM, Casartelli C, Macik BG, Burger NL, Boerwinkle WR, Gourley WK (1983) Establishment and characterization of an in vitro model system for human adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Cancer Res 43: 1703–1709 - PubMed
-
- Buisine MP, Devisme L, Maunoury V, Deschodt E, Gosselin B, Copin MC, Aubert JP, Porchet N (2000) Developmental mucin gene expression in the gastroduodenal tract and accessory digestive glands. I. Stomach. A relationship to gastric carcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem 48: 1657–1666 - PubMed
-
- Byrd JC, Yan P, Sternberg L, Yunker CK, Scheiman JM, Bresalier RS (1997) Aberrant expression of gland-type gastric mucin in the surface epithelium of Helicobacter pylori-infected patients. Gastroenterology 113: 455–464 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

