Protective effect of post-ischaemic viral delivery of heat shock proteins in vivo
- PMID: 18781161
- PMCID: PMC2702130
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2008.106
Protective effect of post-ischaemic viral delivery of heat shock proteins in vivo
Abstract
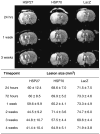
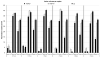
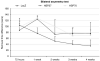
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) function as molecular chaperones involved in protein folding, transport and degradation and, in addition, they can promote cell survival both in vitro and in vivo after a range of stresses. Although some in vivo studies have suggested that HSP27 and HSP70 can be neuroprotective, current evidence is limited, particularly when HSPs have been delivered after an insult. The effect of overexpressing HSPs after transient occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in rats was investigated by delivering an attenuated herpes simplex viral vector (HSV-1) engineered to express HSP27 or HSP70 30 mins after tissue reperfusion. Magnetic resonance imaging scans were used to determine lesion size and cerebral blood flow at six different time points up to 1 month after stroke. Animals underwent two sensorimotor tests at the same time points to assess the relationship between lesion size and function. Results indicate that post-ischaemic viral delivery of HSP27, but not of HSP70, caused a statistically significant reduction in lesion size and induced a significant behavioural improvement compared with controls. This is the first evidence of effective post-ischaemic gene therapy with a viral vector expressing HSP27 in an experimental model of stroke.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of virally delivered HSPs in experimental stroke.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006 Mar;26(3):371-81. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600190. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006. PMID: 16079790
-
Hypothermia decreased the expression of heat shock proteins in neonatal rat model of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2017 May;22(3):409-415. doi: 10.1007/s12192-017-0782-0. Epub 2017 Mar 11. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2017. PMID: 28285429 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of inducible heat shock proteins Hsp27 and Hsp70 in the visual pathway of rats subjected to various models of retinal ganglion cell injury.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 23;9(12):e114838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114838. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25535743 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis versus cell differentiation: role of heat shock proteins HSP90, HSP70 and HSP27.Prion. 2007 Jan-Mar;1(1):53-60. doi: 10.4161/pri.1.1.4059. Epub 2007 Jan 24. Prion. 2007. PMID: 19164900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The protective role of HSP27 in ocular diseases.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jun;49(6):5107-5115. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07222-6. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35212927 Review.
Cited by
-
Chaperones vs. oxidative stress in the pathobiology of ischemic stroke.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Dec 11;17:1513084. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1513084. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39723236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geranylgeranylacetone attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats through the augmentation of HSP 27 phosphorylation: a preliminary study.BMC Neurosci. 2021 Feb 8;22(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12868-021-00614-7. BMC Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33557752 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylated recombinant HSP27 protects the brain and attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption following stroke in mice receiving intravenous tissue-plasminogen activator.PLoS One. 2018 May 24;13(5):e0198039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198039. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29795667 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection of hypoxic postconditioning against global cerebral ischemia through influencing posttranslational regulations of heat shock protein 27 in adult rats.Brain Pathol. 2017 Nov;27(6):822-838. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12472. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Brain Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27936516 Free PMC article.
-
Human-derived physiological heat shock protein 27 complex protects brain after focal cerebral ischemia in mice.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 13;8(6):e66001. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066001. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23785464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acarin L, Paris J, Gonzalez B, Castellano B. Glial expression of small heat shock proteins following an excitotoxic lesion in the immature rat brain. Glia. 2002;38:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Akbar MT, Lundberg AMC, Liu K, et al. The neuroprotective effects of heat shock protein 27 over-expression in transgenic animals against kainate-induced seizures and hippocampal cell death. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:19956–65. - PubMed
-
- Alsop DC, Detre JA. Reduced transit-time sensitivity in non-invasive magnetic resonance imaging of human cerebral blood flow. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996;16:1236–49. - PubMed
-
- Aron Badin R, Lythgoe MF, van der Weerd L, et al. Neuroprotective effects of virally delivered HSPs in experimental stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26:371–81. - PubMed
-
- Aronowski J, Samways E, Strong R, Rhoades HM, Grotta JC. An alternative method for the quantitation of neurological damage after experimental middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats: analysis of behavioural deficit. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996;16:705–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

