Diagnosis of infected total knee: findings of a multicenter database
- PMID: 18781372
- PMCID: PMC2565043
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-008-0471-5
Diagnosis of infected total knee: findings of a multicenter database
Abstract
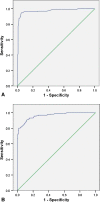
Although total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is an effective and successful procedure, the outcome is occasionally compromised by complications including periprosthetic joint infection (PJI). Accurate and early diagnosis is the first step in effectively managing patients with PJI. At the present time, diagnosis remains dependent on clinical judgment and reliance on standard clinical tests including serologic tests, analysis of aspirated joint fluid, and interpretation of intraoperative tissue and fluid test results. Although reports regarding sensitivity and specificity of all diagnostic tests in the literature are abundant, the interpretation of the available data has been hampered by the low sample size of these studies. In view of the scope of this important problem and the limitations of previous reports, a large database was assembled of all revision TKA performed at three academic referral centers in order to determine the current status of diagnosis of the infected TKA utilizing commonly available tests. Intraoperative cultures should not be used as a gold standard for PJI owing to high percentages of false-negative and false-positive cases. When combined with clinical judgment, total white cell count and percentage of neutrophils in the synovial fluid more accurately reflects PJI and when combined with hematologic exams safely excludes or confirms infection.
Level of evidence: Level II, prognostic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Figures
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.arth.2007.09.005', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2007.09.005'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '18165031', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18165031/'}]}
- Austin MS, Ghanem E, Joshi A, Lindsay A, Parvizi J. A simple, cost-effective screening protocol to rule out periprosthetic infection. J Arthroplasty. 2008;231:65–68. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.arth.2007.03.029', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2007.03.029'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17823025', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17823025/'}]}
- Barrack RL, Aggarwal A, Burnett RS, Clohisy JC, Ghanem E, Sharkey P, Parvizi J. The fate of the unexpected positive intraoperative cultures after revision total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007;226(Suppl 2):94–99. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1054/arth.2000.16504', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1054/arth.2000.16504'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11112192', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11112192/'}]}
- Barrack RL, Engh G, Rorabeck C, Sawhney J, Woolfrey M. Patient satisfaction and outcome after septic versus aseptic revision total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000;158:990–993. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.2106/JBJS.E.01149', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.e.01149'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16595481', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16595481/'}]}
- Bauer TW, Parvizi J, Kobayashi N, Krebs V. Diagnosis of periprosthetic infection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;884:869–882. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/01.blo.0000188066.01833.4f', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/01.blo.0000188066.01833.4f'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16462450', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16462450/'}]}
- Crowninshield RD, Rosenberg AG, Sporer SM. Changing demographics of patients with total joint replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;443:266–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

