Inflicted traumatic brain injury in infants and young children
- PMID: 18782169
- PMCID: PMC8095515
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00204.x
Inflicted traumatic brain injury in infants and young children
Abstract
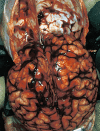
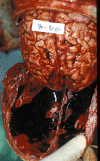
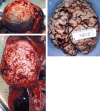
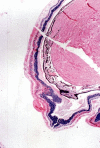
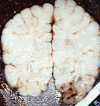
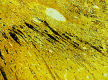
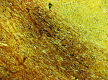
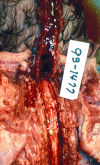
This article will discuss the subject of inflicted or abusive head injury in infants and young children. Inflicted neurotrauma is a very common injury and a frequent problem in attempting to distinguish between inflicted and accidental injury. Inflicted head injury occurs usually in the home in the presence of the individual who has inflicted the injury outside the view of unbiased witnesses. Distinguishing between inflicted and accidental injury may be dependent upon the pathological findings and consideration of the circumstances surrounding the injury. The most common finding in an inflicted head injury is the presence of subdural hemorrhage. Subdural hemorrhage may occur in a variety of distributions and appearances. The natural history of subdural bleeding and the anatomy of the "subdural" will be considered. The anatomy of the dura and its attachment to the skull and to the arachnoid determines how subdural bleeding evolves into the cleaved dural border cell layer and as well as how bridging veins are torn and anatomically where bleeding will occur. Different biomechanical mechanisms result in different distributions of subdural blood and these differences will be discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Adams JH, Graham DI, Murray LS, Scott G (1982) Diffuse axonal injury due to nonmissile head injury in humans. An analysis of 45 cases. Ann Neurol 2:557–563. - PubMed
-
- Adams JH, Doyle D, Ford I, Gennarelli TA, Graham DI, McLellan DR (1989) Diffuse axonal injury in head injury: definition, diagnosis, and grading. Histopathology 15:49–59. - PubMed
-
- Astrup T (1965) Assay and content of tissue thromboplastin in different organs. Thrombosis et Diasthesis Haemorrhagica 14:401–416. - PubMed
-
- Barlow K, Thompson E, Johnson D, Minns RA (2004) The neurological outcome of non‐accidental head injury. Pediatr Rehabil 7:195–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

